Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2018; 24(13): 1373-1385
Published online Apr 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i13.1373
Published online Apr 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i13.1373
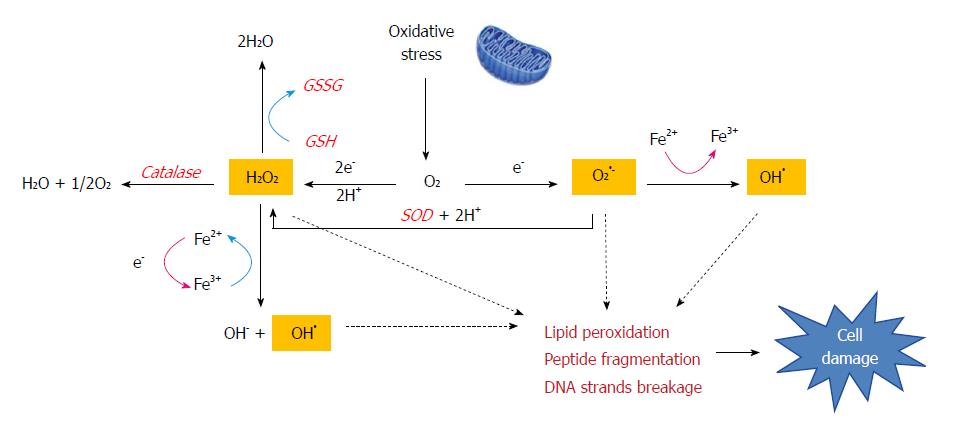
Figure 2 The Fenton reaction in liver disease.
Oxidative stress produces large amounts of reactive compounds and cytotoxic free radicals (H2O2, O2•- and OH•). The Fenton reaction generates hydroxyl radicals (OH•) from hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and superoxide (O2•-) catalyzed by iron. This reaction occurs in cells and free radicals can attack the double bonds of non-saturated phospholipids in cell membranes which eventually degrade the structural integrity of cell membranes, impair enzymatic function and cause cross-linking of proteins or strand breaks in DNA. Cells also have an antioxidant enzyme system (catalase, GSH or SOD) is meant to neutralize free radicals and prevent damage.
- Citation: Ye H, Nelson LJ, Gómez del Moral M, Martínez-Naves E, Cubero FJ. Dissecting the molecular pathophysiology of drug-induced liver injury. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(13): 1373-1385
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i13/1373.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i13.1373