Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2018; 24(1): 87-95
Published online Jan 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i1.87
Published online Jan 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i1.87
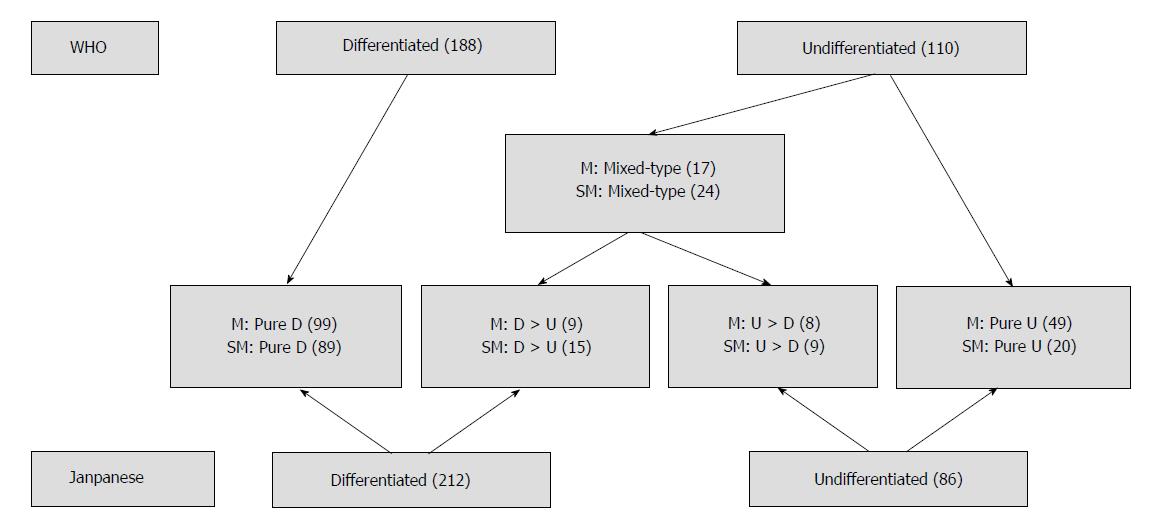
Figure 1 The relationship among the histological classifications of early gastric cancer in the mucosa and submucosa.
Of the 298 cases, there were 212 with differentiated type gastric cancer and 86 with undifferentiated type gastric cancer based on the Japanese classification currently used as the endoscopic resection criteria. In accordance with the WHO classification, there were 188 patients with differentiated type and 110 patients with undifferentiated type gastric cancer. According to the histological differentiation and undifferentiation components, 41 patients were reclassified as mixed-type. For mucosal early gastric cancer (EGC), there were 99 patients in the pure differentiated (pure D) group, 9 in the differentiated > undifferentiated (D > U) group, 8 in the undifferentiated > differentiated (U > D) group, and 49 in the pure undifferentiated (pure U) group. For submucosal EGC, there were 89 in the pure D group, 15 in the D > U group, 9 in the U > D group, and 20 in the pure U group. Among the 41 patients with mixed-type EGC, there were 17 in the mucosa and 24 in the submucosa. D: Differentiated; M: Mucosa; SM: Submucosa; U: Undifferentiated.
- Citation: Zhong Q, Sun Q, Xu GF, Fan XQ, Xu YY, Liu F, Song SY, Peng CY, Wang L. Differential analysis of lymph node metastasis in histological mixed-type early gastric carcinoma in the mucosa and submucosa. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(1): 87-95
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i1/87.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i1.87