Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2018; 24(1): 35-45
Published online Jan 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i1.35
Published online Jan 7, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i1.35
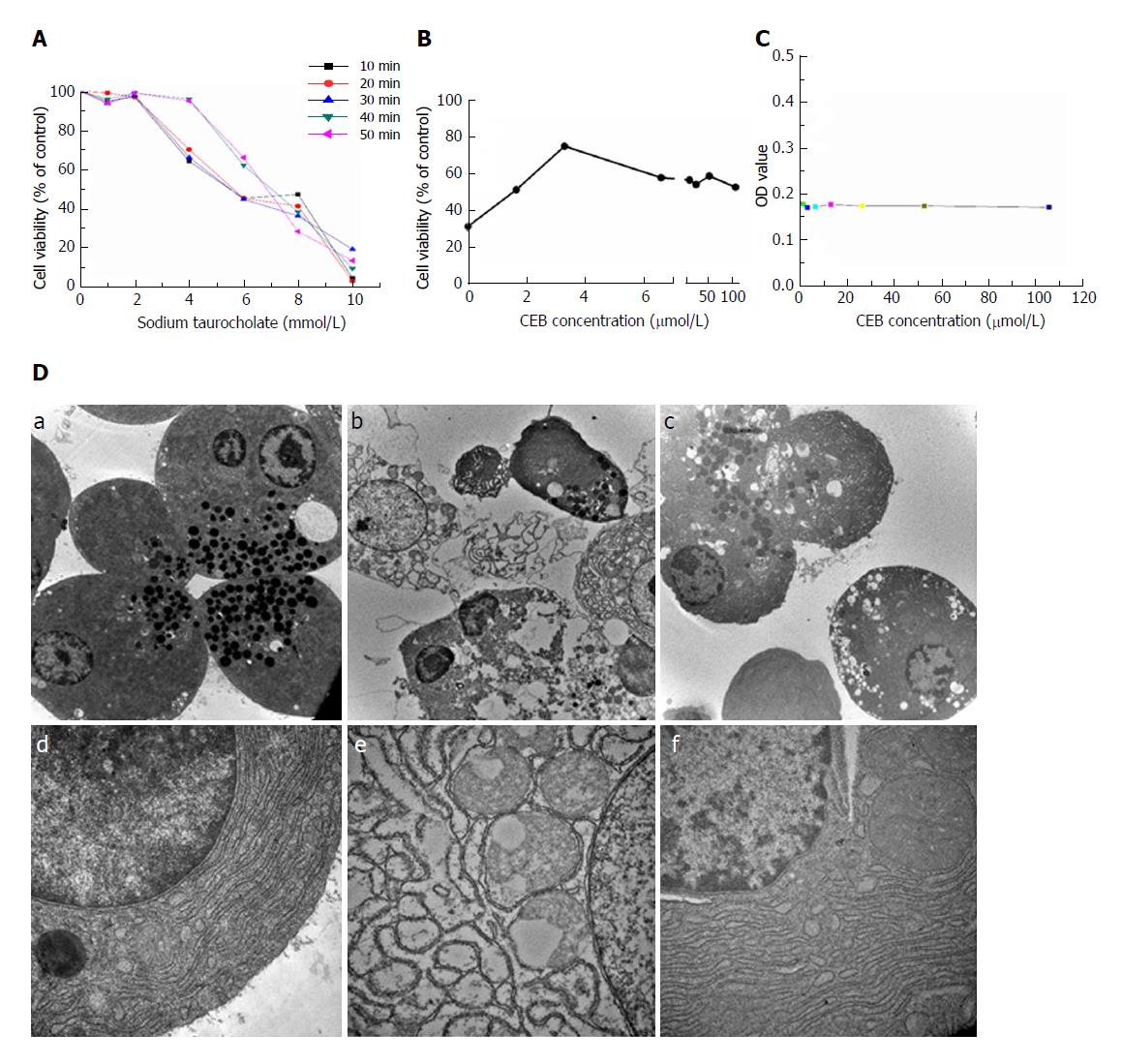
Figure 2 CEB alleviates cell injury in pancreatic acinar cells.
A: The cell viability decreased in a concentration- and time-dependent manner after sodium taurocholate treatment. B: CEB pretreatment increased the viability of cells treated with 8 mM sodium taurocholate and showed dose-dependent protective effects at 1.65-3.3 μmol/L. C: CEB alone had no adverse effect on normal pancreatic acinar cells at either low or high concentration, which suggested its reliability at the cellular level. D: Ultrastructure of pancreatic acinar cells. (a and d) Normal acinar cells showed ZGs concentrated in the apical pole of the cell, slick plasmalemma, and a roundish nucleus in the basal region of the cell. The rough ER was abundant and arranged in the parallel cisternae in the basal region, and numerous ribosomes were present on the membrane of the ER. (b and e) Acinar cells after a 1-min stimulation with sodium taurocholate. Plasmalemma was ruptured, and vacuoles accumulated in the cytoplasm. The ER was dilated and degranulated with lytic membranes. The ZG density also showed a marked reduction. (c and f) Acinar cells preincubated with CEB for 10 min. Vacuolization, cytolysis, and degranulation of ER were significantly alleviated (a-c, ×5000; d-f, ×30000).
- Citation: Li J, Zhou R, Bie BB, Huang N, Guo Y, Chen HY, Shi MJ, Yang J, Zhang J, Li ZF. Emodin and baicalein inhibit sodium taurocholate-induced vacuole formation in pancreatic acinar cells. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(1): 35-45
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i1/35.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i1.35