Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2017; 23(36): 6639-6649
Published online Sep 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6639
Published online Sep 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6639
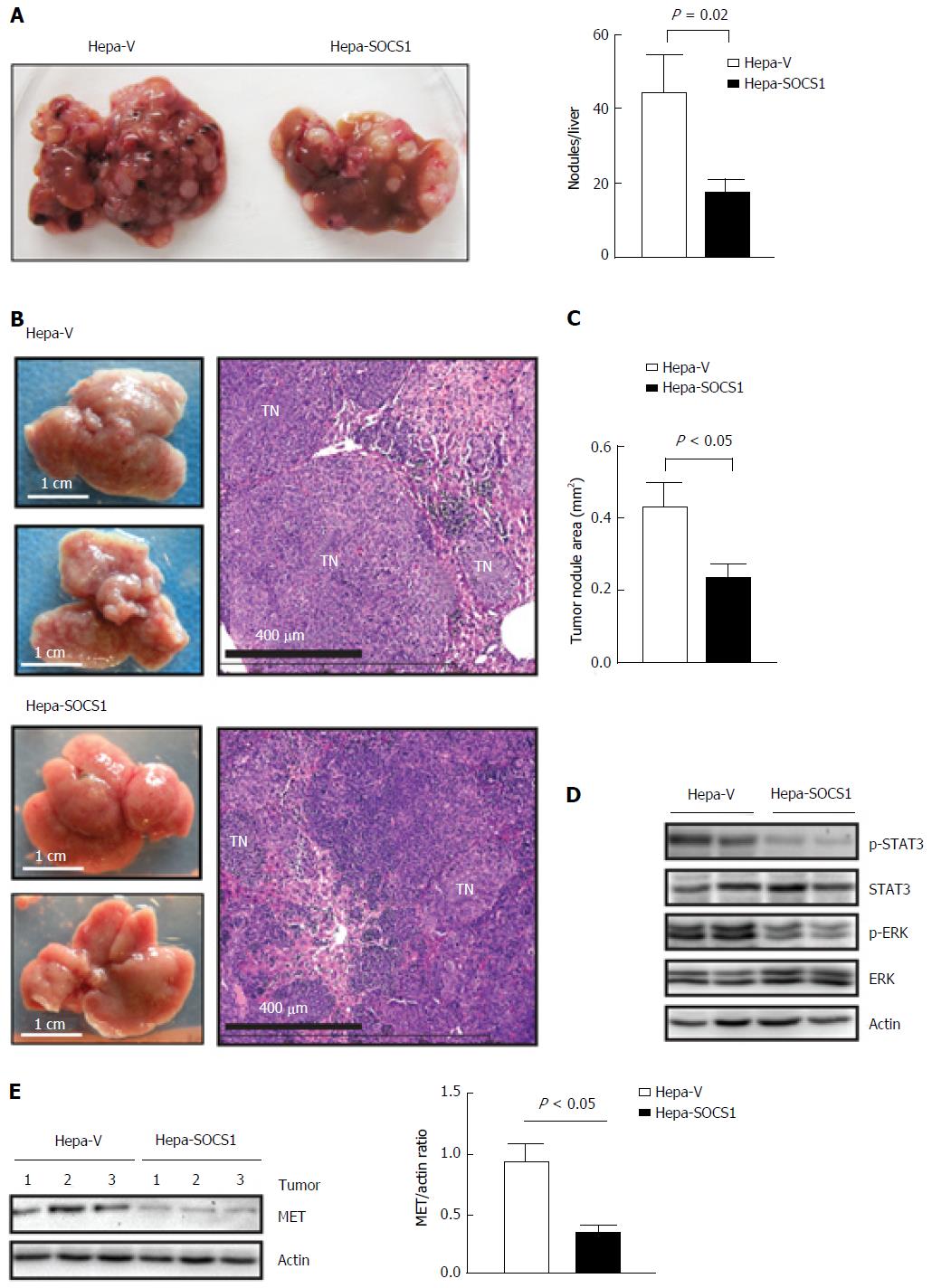
Figure 4 Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 attenuates invasive growth of orthotopic Hepa cell tumors.
A: Hepa-V and Hepa-SOCS1 cells were injected via intravenous route into NOD.scid.gamma (NSG) mice and the livers were examined macroscopically after 20 d. Representative images (left) and quantification of the liver tumor nodules (right) from four mice per group are shown; B-D: Hepa-vector and Hepa-SOCS1 were injected via intrasplenic route into NSG mice (1 × 106 cells per mouse; n = 6 per group from two separate experiments) and the mice were splenectomized. After 20 d, the liver tissues were examined macroscopically for tumor nodules. The dorsal and ventral views of representative livers (B, left) and H and E-stained sections of a representative liver for each group (B, right) are shown; C: For each group, the areas of thirty random tumor nodules from three different mice were measured digitally using the NDP software and compared by Student’s paired t test; D: Western blot evaluation of STAT3 and ERK phosphorylation in the tumors from 2 mice per group; E: Western blot evaluation of MET expression and its quantification in the tumors from 3 mice per group. SOCS1: Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1.
- Citation: Gui Y, Khan MGM, Bobbala D, Dubois C, Ramanathan S, Saucier C, Ilangumaran S. Attenuation of MET-mediated migration and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by SOCS1. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(36): 6639-6649
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i36/6639.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i36.6639