Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2017; 23(34): 6339-6349
Published online Sep 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6339
Published online Sep 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6339
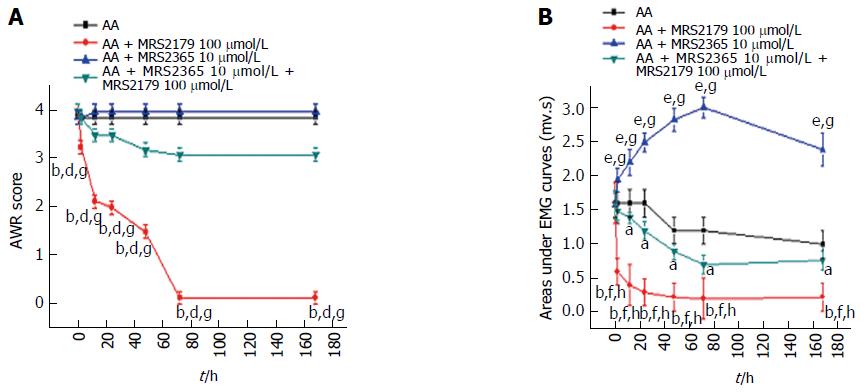
Figure 5 Drug intervention in acetic acid rats.
A: AWR scores showed that MRS2179 could significant decrease the abdominal responses. Differences between the MRS2179 group and the untreated AA rats, MRS2365 group or the combined treatment group were significant. No difference was detected between untreated AA rats and MRS2365 treated rats or rats of the combination group; B: Significant differences of EMG curves were also detected. A significant decrease was detected in the MRS2179 group, which reached a peak at 72 h and continued to persist at 168 h. A significant increase was detected in the MRS2365 group (peaked at 72 h). The difference between the MRS2179 and MRS2365 groups or rats of the combination group was significant. Compared with rats of the combination group, significant differences were detected for untreated AA rats and the MRS2365 group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, eP < 0.001 vs the untreated control group; dP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs the MRS2365 group; gP < 0.01, hP < 0.001 vs the combination group. AWR: Abdominal withdrawal reflex; AUC: Area under the electromyography curve; AA: acetic acid; EMG: Electromyography.
- Citation: Wu J, Cheng Y, Zhang R, Liu D, Luo YM, Chen KL, Ren S, Zhang J. P2Y1R is involved in visceral hypersensitivity in rats with experimental irritable bowel syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(34): 6339-6349
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i34/6339.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i34.6339