Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2017; 23(14): 2556-2565
Published online Apr 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i14.2556
Published online Apr 14, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i14.2556
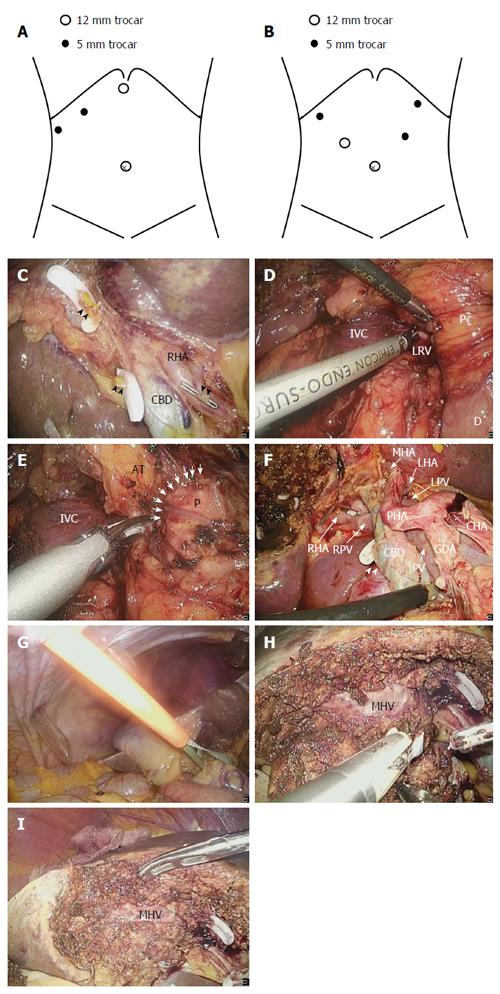
Figure 3 Surgical procedure for laparoscopic gallbladder bed resection.
A: Position of trocars in laparoscopic gallbladder bed resection (LCGB) with D1 lymphadenectomy; B: Position of trocars in LCGB with D2 lymphadenectomy; C: The cystic artery and duct are cut at their origin; D: Kocher’s mobilization; E: Lymph node dissection around the posterosuperior region of the pancreas head. Arrow indicates the boundary between the pancreatic parenchyma and surrounding adipose tissues; F: Completion of D2 lymphadenectomy; G: Performance of the Pringle maneuver with an extracorporeal tourniquet; H: Transection of the liver parenchyma by the clamp crushing method; I: After the gallbladder bed resection. RHA: Right hepatic artery; CBD: Common bile duct; Arrowhead: Stump of the cystic duct; Dotted arrow: Stump of the cystic artery; P: Pancreatic head; D: Duodenum; IVC: Inferior vena cava; LRV: Left renal vein; AT: Adipose tissues; GDA: Gastroduodenal artery; CHA: Common hepatic artery; PHA: Proper hepatic artery; LHA: Left hepatic artery; MHA: Middle hepatic artery; PV: Portal vein; LPV: Left portal vein; RPV: Right portal vein; MHV: Middle hepatic vein.
- Citation: Ome Y, Hashida K, Yokota M, Nagahisa Y, Okabe M, Kawamoto K. Laparoscopic approach to suspected T1 and T2 gallbladder carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(14): 2556-2565
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i14/2556.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i14.2556