Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2017; 23(11): 1944-1953
Published online Mar 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i11.1944
Published online Mar 21, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i11.1944
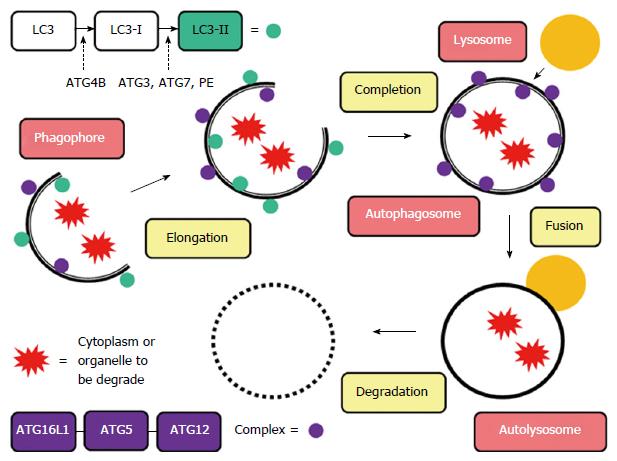
Figure 1 Autophagy mechanism.
The autophagy pathway. During this process, the endoplasmic reticulum or other membranous cellular structures respond to stimuli by generating a double-membrane structure called a phagophore. On this phagophore, ATG16L1 forms a complex with an ATG5-ATG12 conjugate, which multimerizes and then lipidates LC3 (LC3-II). Simultaneously, the phagophore elongates to envelop the cytoplasm or organelle to be degraded, forming an autophagosome, a unique double-membrane organelle. The outer membrane of the autophagosome then fuses with a lysosome to form an autolysosome, and the inner membrane degrades and absorbs its contents.
- Citation: Iida T, Onodera K, Nakase H. Role of autophagy in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(11): 1944-1953
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i11/1944.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i11.1944