Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 28, 2016; 22(8): 2512-2523
Published online Feb 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2512
Published online Feb 28, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2512
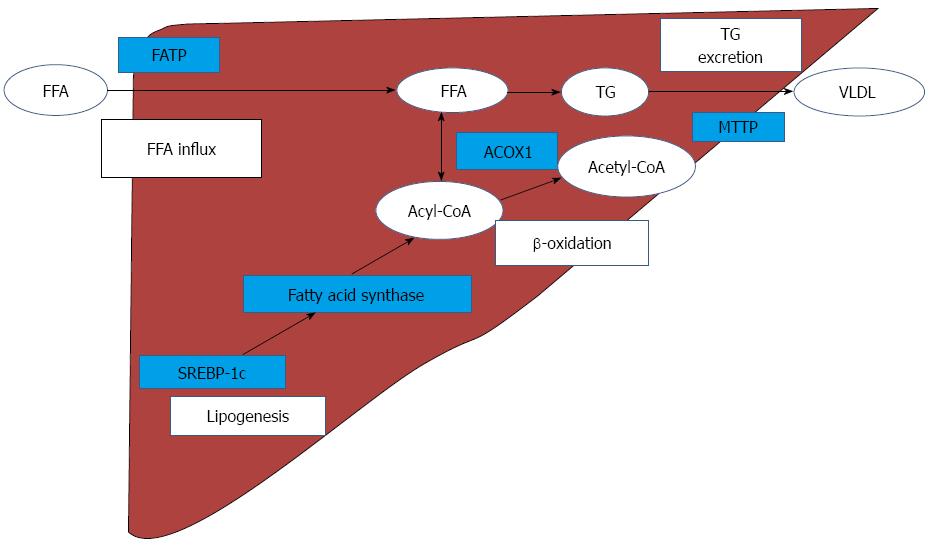
Figure 5 Predicted mechanism of hepatic lipid metabolism on methionine-choline-deficient diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitismodel.
MCD increases FATP in the liver and hepatic FFA contents are increased. SREBP-1c modulates fatty acid synthase, and facilitates hepatic de novo lipogenesis. Fatty acid synthase produces Acyl-CoA which is catalyzed by ACOX1 in β-oxidation. Accumulated FFA is stored in hepatocytes as TG, and hepatic TG are excreted by MTTP, as VLDL. MCD: Methionine-choline-deficient diet; FATP: Fatty acid transport protein; FFA: Free fatty acid; SREBP-1c: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c; ACOX1: Acyl-coenzyme A oxidase 1; TG: Triglyceride; MTTP: Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein; VLDL: Very low density lipoprotein.
- Citation: Yamamoto T, Nakade Y, Yamauchi T, Kobayashi Y, Ishii N, Ohashi T, Ito K, Sato K, Fukuzawa Y, Yoneda M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue prevents nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in non-obese mice. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(8): 2512-2523
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i8/2512.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2512