Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2016; 22(45): 9954-9965
Published online Dec 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9954
Published online Dec 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9954
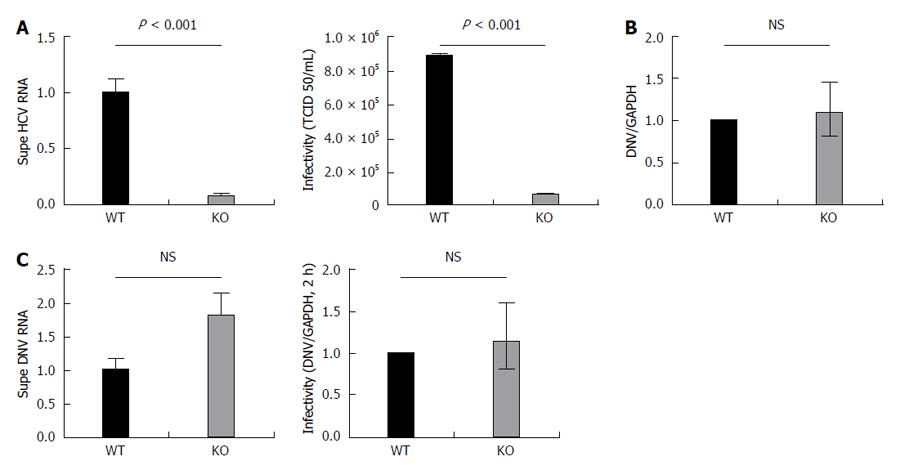
Figure 4 APOB KO cells have diminished hepatitis C virus production and KO virus has impaired infectivity, but APOB KO has no effect on dengue viral infection.
A: 72 h following infection with JFH1 hepatitis C virus (HCV)cc, supernatant was harvested and viral RNA was isolated and quantified using qPCR. The supernatant harvested from infected KO cells had significantly lower levels of HCV RNA compared to WT supernatant. Data are normalized to WT RNA titer and standard error of the mean shown. After normalizing for the differences in HCV RNA by diluting the WT virus, the infectivity of the two viruses in highly HCV-permissive Huh 7.5.1 cells was then determined using the TCID50 method. The KO generated virus had significantly reduced infectivity in the permissive Huh 7.5.1 cells; B: Dengue replication: WT and KO cells were infected with Dengue virus, and the level of intracellular RNA was assessed at 72 h. No difference was observed between WT and KO cells. Data is shown as mean with 95% confidence interval, normalized to WT; C: Supernatant of dengue-infected cells was harvested at 72 h and dengue viral RNA quantified. RNA levels were slightly higher in the supernatant of the KO cells, but the difference was not significant. A similar trend was observed with the infectivity of the KO generated dengue virus, assessed at DNV RNA at 2 h following infection.
- Citation: Schaefer EAK, Meixiong J, Mark C, Deik A, Motola DL, Fusco D, Yang A, Brisac C, Salloum S, Lin W, Clish CB, Peng LF, Chung RT. Apolipoprotein B100 is required for hepatitis C infectivity and Mipomersen inhibits hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(45): 9954-9965
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i45/9954.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9954