Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2016; 22(45): 9954-9965
Published online Dec 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9954
Published online Dec 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9954
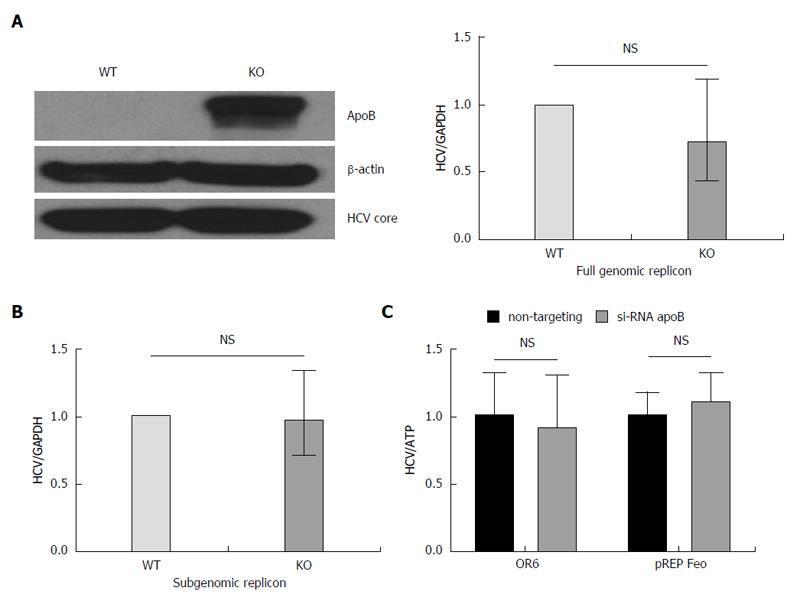
Figure 3 Loss of apoB does not impair replication in APOB KO cells.
A: A full genomic replicon derived from the JFH1 hepatitis C virus (HCV)cc strain was electroporated into WT and KO cells which were then selected in culture based on antibiotic resistance. We demonstrated that there was no decrease in intracellular HCV core or RNA in the KO compared to WT cells; B: A subgenomic replicon, which lacks expression of the E1, E2 and core proteins, was also electroporated into the cells and again there was no difference in HCV RNA. Data is shown as mean with 95%CI, normalized to WT; C: To confirm these findings, we used replicon cells with a full genome of a different viral genotype (OR6, 1b and pREP-Feo, 1b) and subsequently knocked down apoB expression using RNAi. There was no difference in HCV replication in the setting of apoB knockdown. Data is shown as mean ± SD.
- Citation: Schaefer EAK, Meixiong J, Mark C, Deik A, Motola DL, Fusco D, Yang A, Brisac C, Salloum S, Lin W, Clish CB, Peng LF, Chung RT. Apolipoprotein B100 is required for hepatitis C infectivity and Mipomersen inhibits hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(45): 9954-9965
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i45/9954.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i45.9954