Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2016; 22(35): 7926-7937
Published online Sep 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i35.7926
Published online Sep 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i35.7926
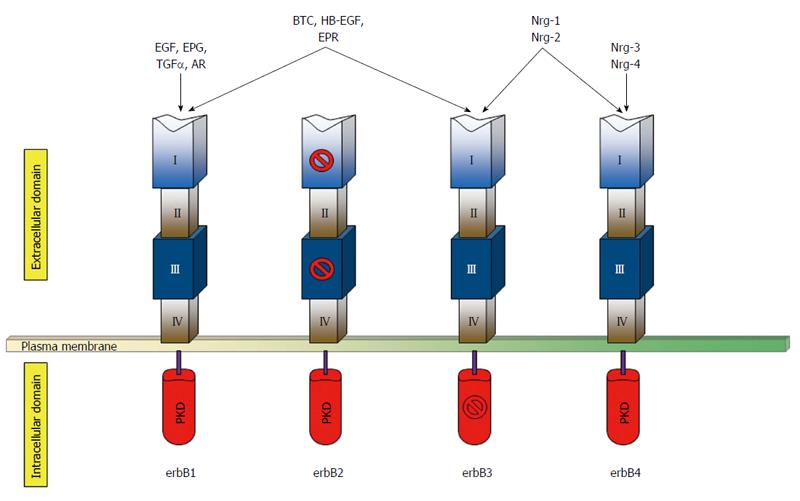
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the human erbB receptors in basal condition.
The extracellular portion of each receptor consists of four domains (I-IV). Both domains I and III, which are related leucine-rich segments, actively participate in ligand binding, except for those of erbB2. Domains II and IV contain numerous cysteine residues and participates in dimer formation. The kinase domain of erbB3 is kinase-impaired. The growth factor groups that bind each receptor are indicated on the top. PKD: Protein kinase domain; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; EPG: Epigen; TGFα: Transforming growth factor-α; AR: Amphiregulin; BTC: Betacellulin; HB-EGF: Heparin-binding epidermal growth-factor like growth factor; EPR: Epiregulin; Nrg-1/2/3/4: Neuregulin-1/2/3/4.
- Citation: Fusco N, Bosari S. HER2 aberrations and heterogeneity in cancers of the digestive system: Implications for pathologists and gastroenterologists. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(35): 7926-7937
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i35/7926.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i35.7926