Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2016; 22(3): 1213-1223
Published online Jan 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1213
Published online Jan 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1213
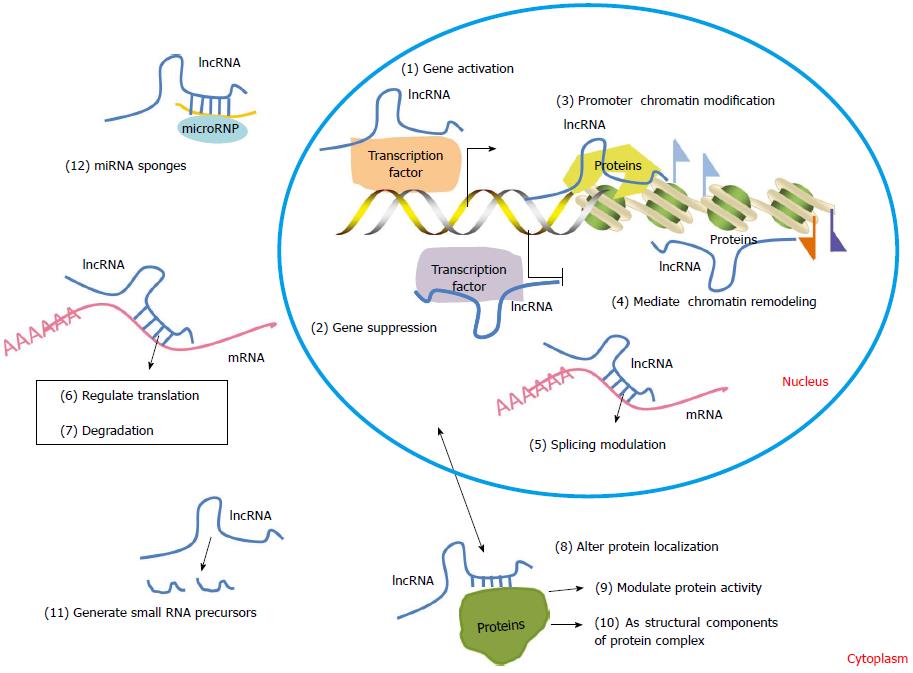
Figure 3 Functions of lncRNAs.
Individual lncRNA transcription occurs at a specific time and place to integrate developmental cues, interpret cellular context, or respond to diverse stimuli. A number of lncRNAs bind to and titrate away transcription factors to activate or suppress gene expression (1, 2); some lncRNAs guide site-specific recruitment of chromatin-modifying complexes to genomic sites to induce epigenetic changes and regulate gene expression (3); several lncRNAs serve as scaffolds for chromatin-modifying complexes (4); some lncRNAs specifically interact with complementary mRNAs that modulate various processes of post-transcription, such as splicing, translation and degradation (5-7). A number of lncRNAs are able to alter protein localization, regulate protein activity, or act as components of protein complex (8-10). Some lncRNAs appear to generate small RNA precursors or function as miRNA sponges (11, 12).
- Citation: Xie SS, Jin J, Xu X, Zhuo W, Zhou TH. Emerging roles of non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer: Pathogenesis and clinical implications. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(3): 1213-1223
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i3/1213.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1213