Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2016; 22(29): 6690-6705
Published online Aug 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i29.6690
Published online Aug 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i29.6690
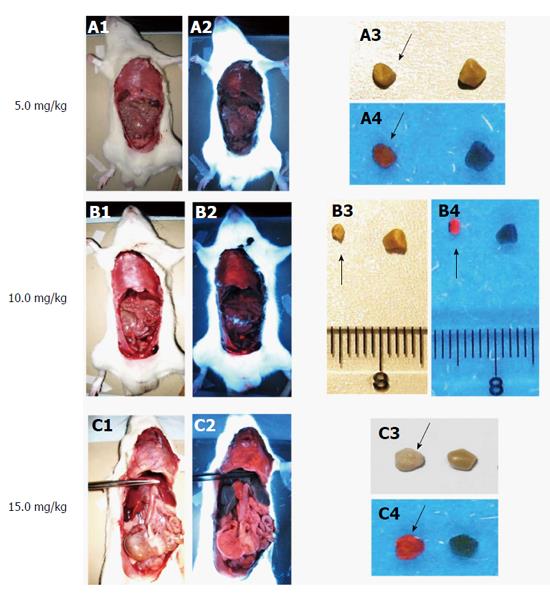
Figure 7 Macroscopic digital imaging under white and UV (365 nm) lights in rats of cholelithiasis receiving intravenous 1 × 10-3 M hypericin at 5, 10, 15 mg/kg and their corresponding extracted gallstones.
Rats receiving hypericin at 5 mg/kg (A1) exhibited almost no fluorescence in organs (A2). The extracted gallstones (black arrow) showed faint fluorescent relative to control stones (A3, A4). With 10 mg/kg hypericin (B1), moderate fluorescence appeared in the diaphragm (B2). Higher red fluorescence in gallstones (black arrow) was observed as compared to control stone (B3, B4). Rats treated with 15 mg/kg hypericin (C1) revealed high fluorescence in visceral organs (C2). The stone (black arrow) displayed high fluorescence as compared to the control (C3, C4).
- Citation: Miranda Cona M, Liu YW, Hubert A, Yin T, Feng YB, de Witte P, Waelkens E, Jiang YS, Zhang J, Mulier S, Xia Q, Huang G, Oyen R, Ni YC. Differential diagnosis of gallstones by using hypericin as a fluorescent optical imaging agent. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(29): 6690-6705
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i29/6690.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i29.6690