Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2016; 22(26): 5971-6007
Published online Jul 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i26.5971
Published online Jul 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i26.5971
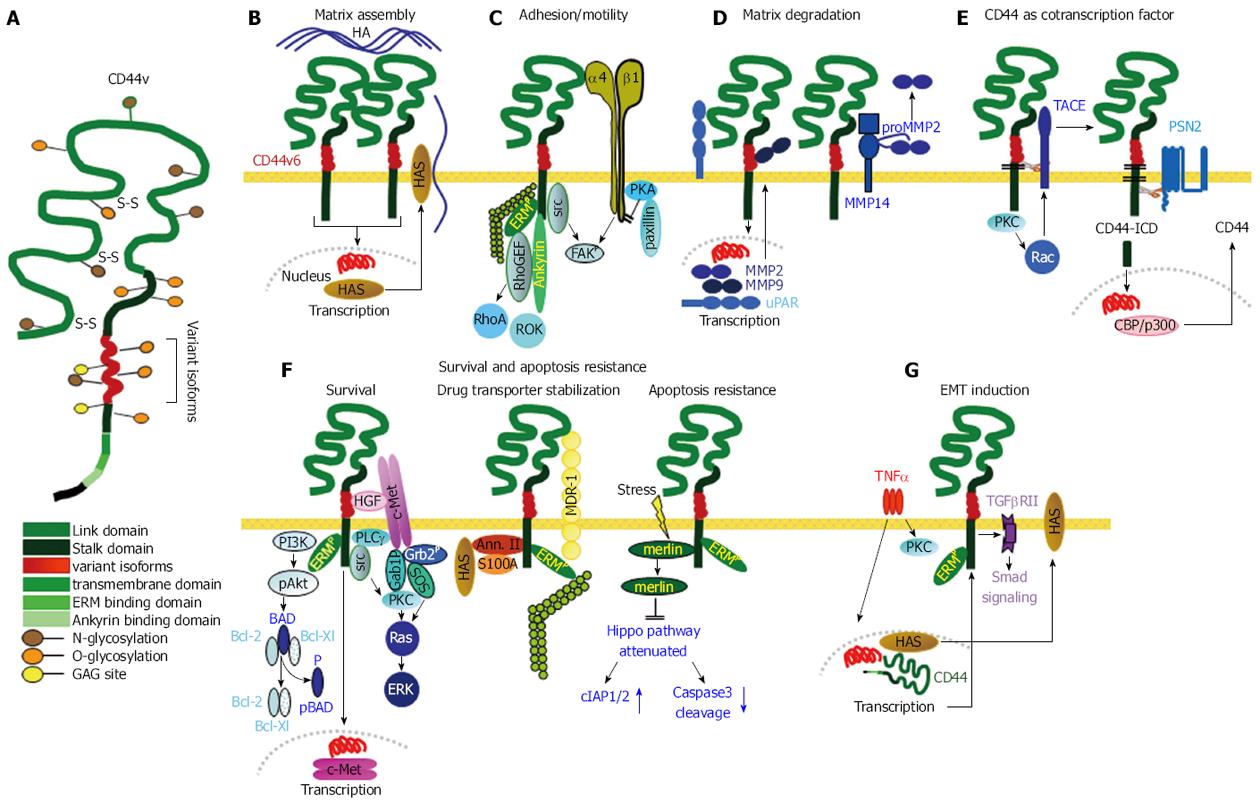
Figure 2 Cancer stem cells supporting activities of CD44v6.
A: Structure of CD44 including insertion of variant exon products; B: CD44v6 is engaged in assembling the HA matrix by inducing HAS transcription. The matrix supports CD44 activation; C: GEM-located CD44/CD44v6 is src associated and cooperates with adjacent integrins. Activated ERM proteins and Ankyrin link CD44 to the cytoskeleton and initiate RhoA and ROK activation, which together play an important role in CSC motility; D: CD44v6 is engaged in uPAR and MMP transcription. It associates with MMP14, which captures MMP2 and MMP9, supporting ECM degradation and remodeling; E: GEM-located CD44v6 can be cleaved by TACE and subsequently by PSN2. CD44-ICD is a powerful cotranscription factor, which induces beside others CD44 transcription; F: There are several pathways, whereby CD44v6 supports CSC survival and apoptosis resistance. It cooperates with c-Met, which is brought into vicinity by CD44v6-bound HGF; a complex of CD44, Annexin II, S100A and HAS stabilizes MDR1; stress induces merlin phosphorylation, which dissociates from CD44 and hampers activation of the Hippo pathway; G: One pathway of CD44-linked induction of EMT relies on TNFα that fosters CD44 expression and CD44 cooperativity with TGFβRII promoting Smad signaling. CD44 also is engaged in activation of Nanog and in repressing miRNA transcription that targets EMT proteins (not shown). The majority of these CSC supporting activities of CD44/CD44v6 rely on GEM-recruited CD44. CSC: Cancer stem cells; GEM: Glycolipid-enriched microdomains; ERM: Cytoskeletal proteins ezrin, radixin, moesin; EMT: Epithelial mesenchymal transition; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor α; TGFβ: Transforming growth factor β; TACE: TNFα converting enzyme.
- Citation: Heiler S, Wang Z, Zöller M. Pancreatic cancer stem cell markers and exosomes - the incentive push. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(26): 5971-6007
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i26/5971.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i26.5971