Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2015; 21(46): 13055-13063
Published online Dec 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i46.13055
Published online Dec 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i46.13055
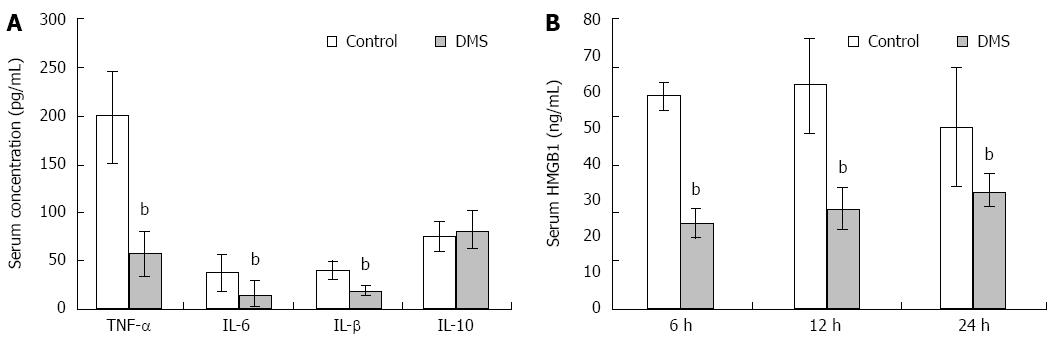
Figure 4 Inhibition of SPHK1 activation downregulates serum inflammatory cytokine and HMGB1 levels in mice with acute liver failure.
A: DMS reduced serum levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 significantly (57.07 pg/mL ± 22.83 pg/mL vs 198.55 pg/mL ± 48.17 pg/mL; 15.66 pg/mL ± 13.13 pg/mL vs 37.44 pg/mL ± 18.68 pg/mL; 19.13 pg/mL ± 5.32 pg/mL vs 40.13 pg/mL ± 9.37 pg/mL, t = 27.6, 10.12 and 4.33, respectively, bP < 0.01), but did not increase the level of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 at 12 h; B DMS reduced HMGB1 levels at 6, 12, and 24 h in mice (23.49 ng/mL ± 3.89 ng/mL vs 58.6 ng/mL ± 3.65 ng/mL; 61.62 ng/mL ± 13.07 ng/mL vs 27.32 ng/mL ± 5.97 ng/mL; 49.91 ng/mL ± 16.6 ng/mL vs 32.42 ng/mL ± 4.23 ng/mL, t = 11.27, 4.07, and 8.42, respectively, bP < 0.01). The mean ± SE of three independent experiments is shown (error bar indicates standard error).
- Citation: Lei YC, Yang LL, Li W, Luo P, Zheng PF. Inhibition of sphingosine kinase 1 ameliorates acute liver failure by reducing high-mobility group box 1 cytoplasmic translocation in liver cells. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(46): 13055-13063
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i46/13055.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i46.13055