Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2015; 21(41): 11552-11566
Published online Nov 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i41.11552
Published online Nov 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i41.11552
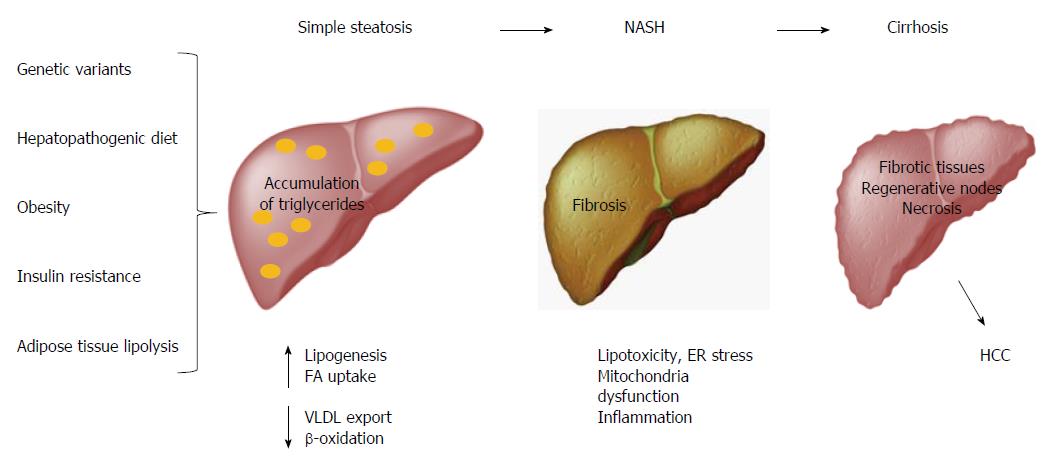
Figure 3 Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease pathogenesis.
The spectrum of NAFLD includes simple steatosis, NASH, LC and even HCC. Risk factors such as obesity, hepatopathogenic diet, insulin resistance and adipose tissue lipolysis lead to accumulation of triglycerides. This abnormality can stimulate lipotoxicity, ER stress, mitochondria dysfunction and inflammation, promoting fibrosis. Chronic fibrogenesis causes histological changes in the liver that lead to LC, which in turn may evolve to HCC. NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; LC: Liver cirrhosis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; FA: Fatty acids; VLDL: Very low-density lipoprotein; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum.
- Citation: Ramos-Lopez O, Martinez-Lopez E, Roman S, Fierro NA, Panduro A. Genetic, metabolic and environmental factors involved in the development of liver cirrhosis in Mexico. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(41): 11552-11566
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i41/11552.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i41.11552