Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2015; 21(34): 9982-9992
Published online Sep 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9982
Published online Sep 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9982
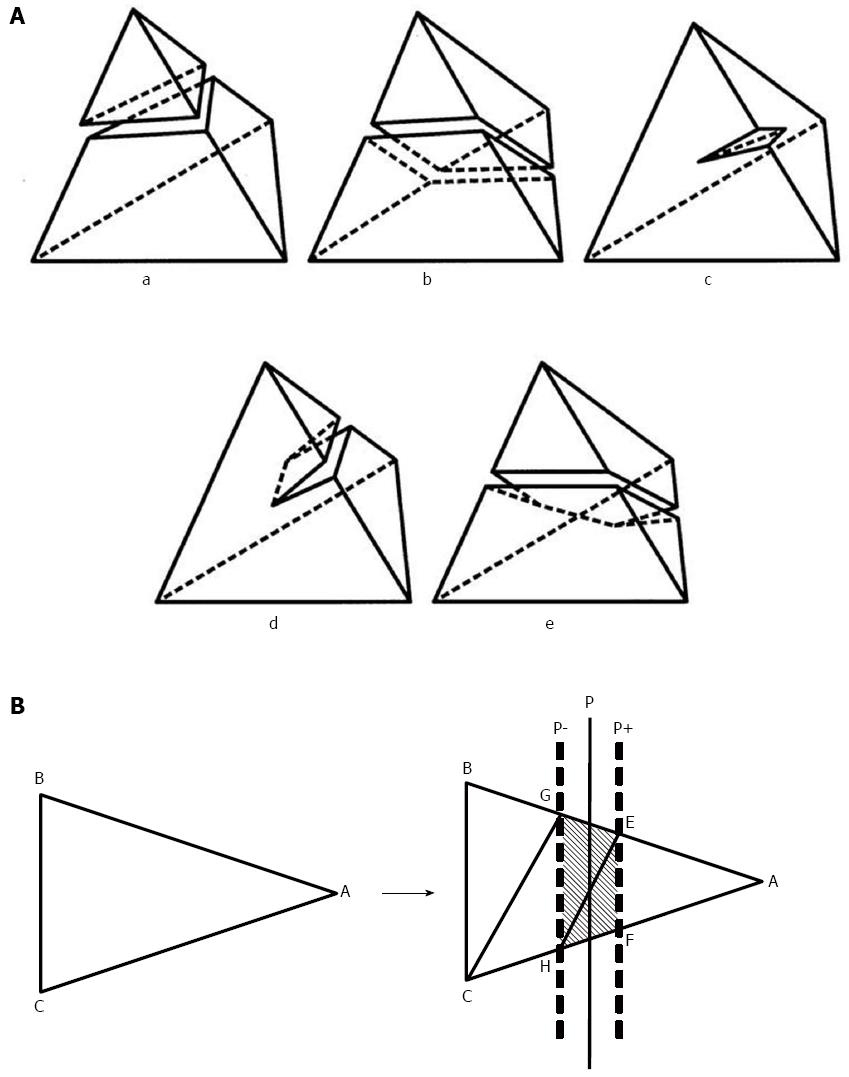
Figure 2 Incision function.
A: The incision function of the liver parenchyma. Incision functions are implemented at the top of the Sofa framework. This function is used for cutting the tetrahedral meshes used in the incisions of the liver parenchyma. The patterns used for cutting the tetrahedral meshes were divided into five types; B: A typical example of triangle subdivision. The triangle ABC above is subdivided by two sheets of cut planes, P+ and P-, into five triangles: AEF, EFH, EHG, GHC, and GCB, as below. Planes P+ and P- are defined by the slightly translating plane P, which cuts the tetrahedrons. Each of the triangles plays a different role. The three triangles between P+ and P- are exposed on the outside of the liver during simulation, whereas the other two are placed inside. Liversim allows the user to delete the exposed triangles to simulate the process of removing the exposed vessels in the cut surface of the liver. Using these functions, a user can cut open the liver parenchyma and remove the exposed segments of the hepatic vessels.
- Citation: Oshiro Y, Yano H, Mitani J, Kim S, Kim J, Fukunaga K, Ohkohchi N. Novel 3-dimensional virtual hepatectomy simulation combined with real-time deformation. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(34): 9982-9992
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i34/9982.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9982