Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2015; 21(34): 9853-9862
Published online Sep 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9853
Published online Sep 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9853
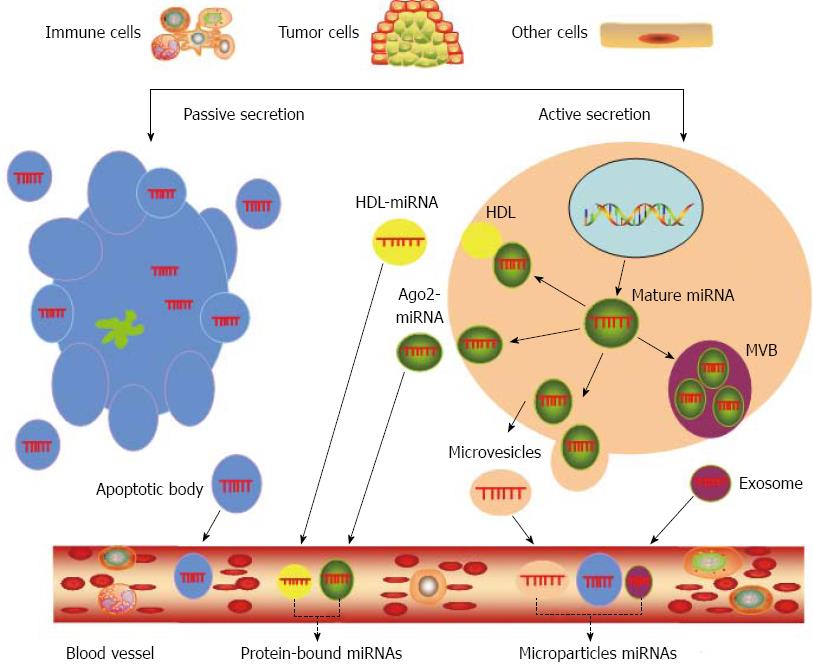
Figure 2 Mechanisms of microRNAs secretion into blood vessels; origins and types of circulating microRNAs.
miRNAs can be secreted from living cells into the extracellular environment (such as blood vessels) via the following mechanisms: (1) active secretion via exosomes; (2) active secretion via microvesicles; (3) active secretion in protein-miRNA complex (Ago2) and lipoprotein complex (such as HDL); and (4) passive secretion through apoptotic bodies. Circulating miRNAs may originate from immune cells, endothelial cells of other organs, and cancer-specific cells. In the blood, miRNAs can circulate as circulating protein-bound miRNAs or circulating microparticle miRNAs. Three types of microparticles are found in circulating blood: exosomes, microvesicles and apoptotic body. Circulating miRNAs are also present as protein-bound miRNAs. These miRNAs are primarily associated with specific RNA-bind proteins and lipoproteins, such as Ago2 and HDL. AGO: Argonaute; HDL: High-density lipoprotein; miRNAs: MicroRNAs; MVB: Multivesicular body.
- Citation: Zhang YC, Xu Z, Zhang TF, Wang YL. Circulating microRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic tools for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(34): 9853-9862
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i34/9853.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9853