Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2015; 21(20): 6180-6193
Published online May 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6180
Published online May 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6180
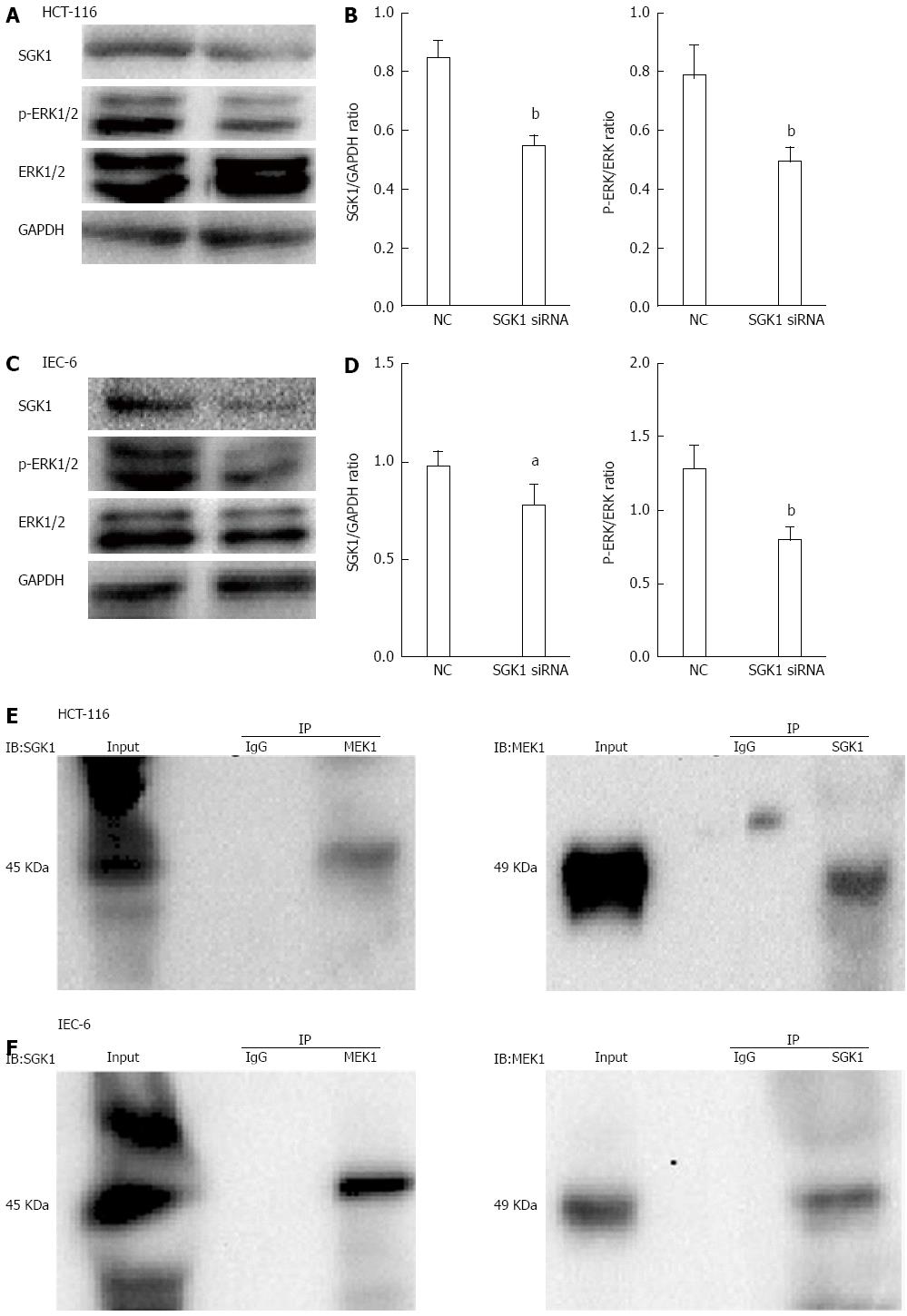
Figure 6 Efficiency of serum-and-glucocorticoid-inducible-kinase-1 silencing after serum-and-glucocorticoid-inducible-kinase-1 siRNA transfection and co-immunoprecipitation of serum-and-glucocorticoid-inducible-kinase-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1.
A, B: The efficiency of SGK1 silencing the subsequent dysregulation of p-ERK and ERK in HCT-116 cells. The efficiency of SGK1 silencing was assessed by the ratio of SGK1/GAPDH. The level of ERK phosphorylation was assessed by the ratio of p-ERK/ERK; C, D: The efficiency of SGK1 silencing and the following dysregulation of p-ERK and ERK in IEC-6 cells. The NC group served as controls. GAPDH served as the internal control; E, F: SGK1 was co-immunoprecipitated with MEK1 on IECs. HCT-116 and IEC-6 cell lysates were subjected to co-immunoprecipitation with anti-SGK1 or control IgG and were detected with anti-MEK1 antibodies. MEK1 was co-immunoprecipitated with SGK1. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs negative controls.
-
Citation: Bai JA, Xu GF, Yan LJ, Zeng WW, Ji QQ, Wu JD, Tang QY. SGK1 inhibits cellular apoptosis and promotes proliferation
via the MEK/ERK/p53 pathway in colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(20): 6180-6193 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i20/6180.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6180