Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2015; 21(16): 4852-4863
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.4852
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.4852
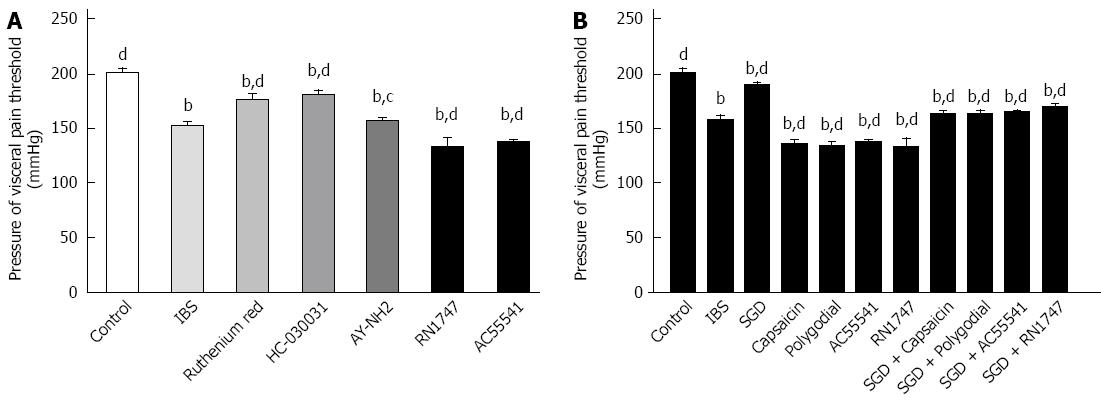
Figure 4 Transient receptor potential channels and protease-activated receptors involved in water avoidance stress-induced visceral hyperalgesia.
A: TRP channels and PARs involved in WAS-induced VHL; B: TRP channels and PARs involved in the effect of SGD on VHL. The blockers or activators of TRP channels and PARs were given by intraperitoneal injection after WAS on day 10. One hour later, rats were subjected to colorectal distension and AWR pressure threshold measurement. Ruthenium Red: blocker of TRPV1, 5 mg/kg; HC-030031: blocker of TRPA1, 5 mg/kg; AY-NH2: activator of PAR4, 1 mg/kg; RN1747: activator of TRPV4, 5 mg/kg; AC55541: activator of PAR2, 0.78 mg/kg; capsaicin: activator of TRPV1, 5 mg/kg; Polygodial: activator of TRPA1, 5 mg/kg. Ruthenium Red was dissolved in distilled water. Other blockers or activators were dissolved in 10% dimethylsulfoxide/5% Tween 80/ 85% saline. Data are presented as mean ± SD, bP < 0.01 vs control; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs IBS. Statistical comparisons were performed using One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test using GraphPad Prism 5.0. (n = 5-7). TRP: Transient receptor potential; PAR: protease-activated receptor; WAS: Water avoidance stress; VHL: Visceral hyperalgesia; IBS: Irritable bowel syndrome; SGD: Shugan decoction.
- Citation: Shi HL, Liu CH, Ding LL, Zheng Y, Fei XY, Lu L, Zhou XM, Yuan JY, Xie JQ. Alterations in serotonin, transient receptor potential channels and protease-activated receptors in rats with irritable bowel syndrome attenuated by Shugan decoction. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(16): 4852-4863
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i16/4852.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.4852