Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2015; 21(16): 4840-4851
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.4840
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.4840
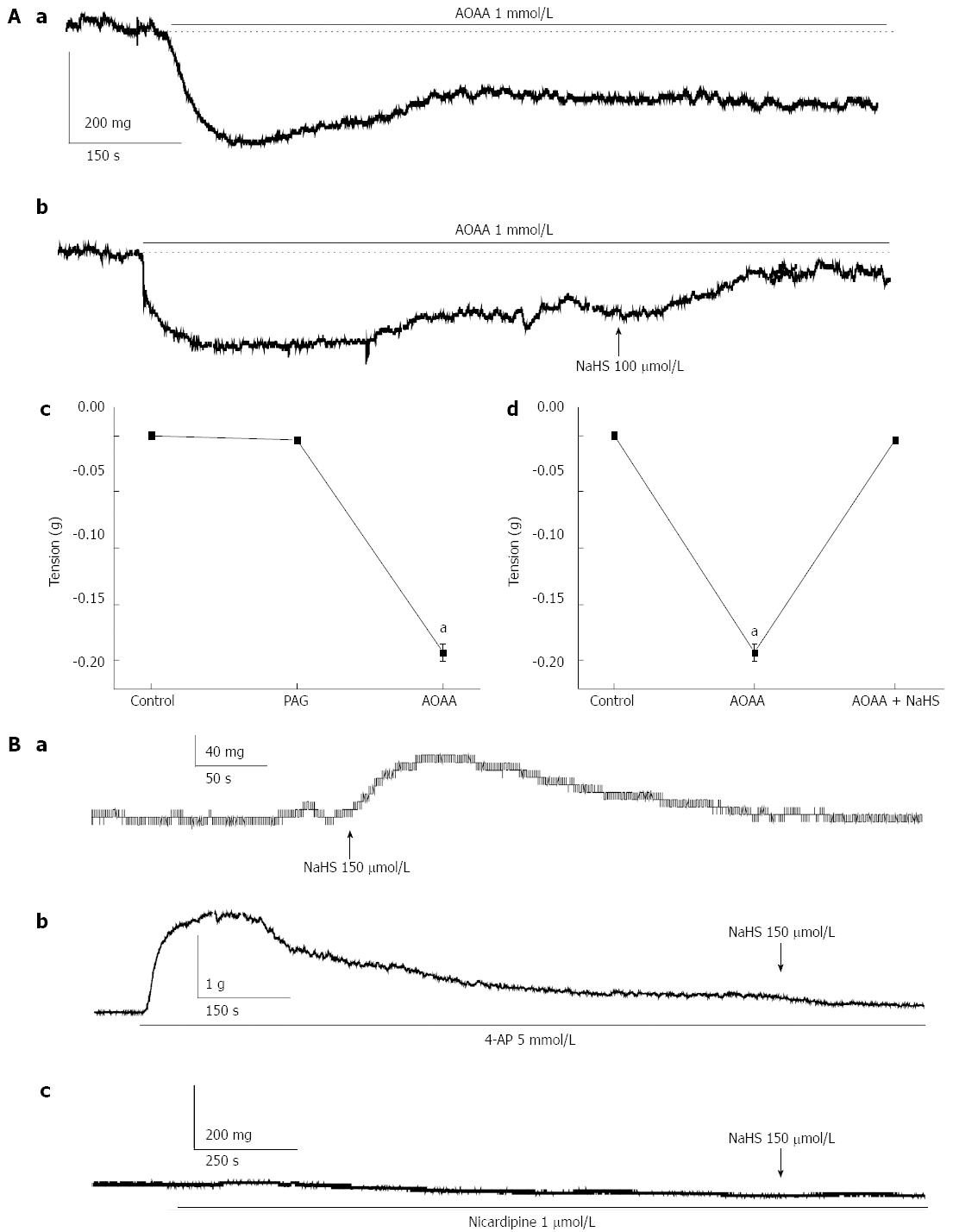
Figure 3 Effects of aminooxyacetic acid, DL-propargylglycine and ion channel blockers on NaHS-induced gastric fundus smooth muscle tonic contraction.
A: Effects of AOAA and PAG on gastric fundus smooth muscle basal tension (a, b: H2S significantly recovered the AOAA-induced decrease in basal tension; c: Summarized graph showing the changes in AOAA- and PAG-induced tonic contractions; d: The recovery effect of NaHS on the AOAA-induced decrease in gastric fundus smooth muscle tension); B: Effects of a potassium channel blocker and L-type calcium channel blocker on NaHS-induced tonic contraction (a: Representative traces of NaHS-induced tonic contraction; b,c: Effect of 4-AP (5 mmol/L) on NaHS-induced tonic contraction, and effect of nicardipine (1μmol/L) on NaHS-induced tonic contraction. Data are expressed as mean ± SE, n = 10, aP < 0.05, vs the control. AOAA: Aminooxyacetic acid; PAG: DL-propargylglycine.
- Citation: Meng XM, Huang X, Zhang CM, Liu DH, Lu HL, Kim YC, Xu WX. Hydrogen sulfide-induced enhancement of gastric fundus smooth muscle tone is mediated by voltage-dependent potassium and calcium channels in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(16): 4840-4851
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i16/4840.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.4840