Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2015; 21(15): 4583-4591
Published online Apr 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i15.4583
Published online Apr 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i15.4583
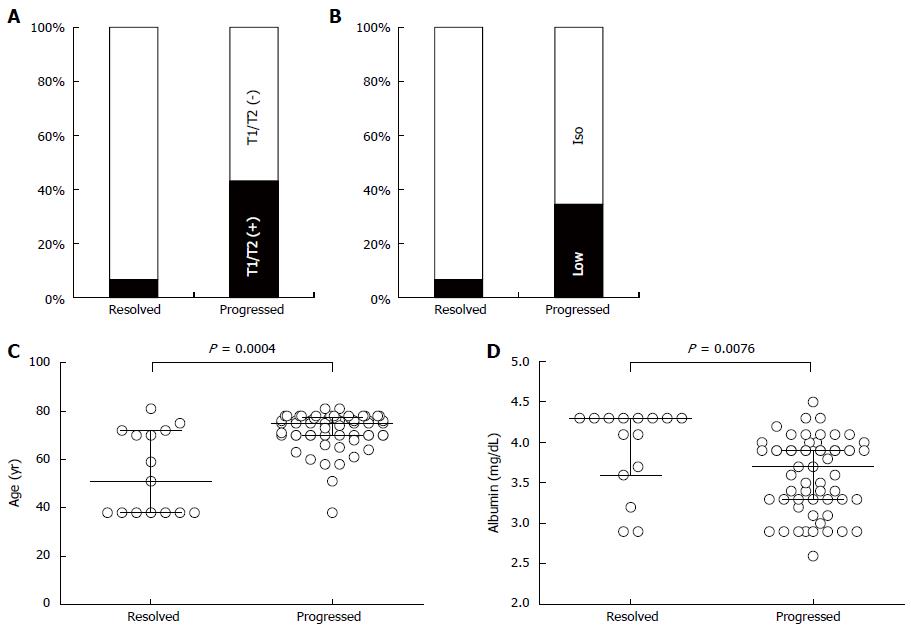
Figure 4 Characteristics of non-hypervascular nodules clarified by univariate analyses.
Non-hypervascular nodules (NHNs) that were detected in the hepatobiliary phase of gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylene-triamine-pentaacetic-acid magnetic resonance imaging were univariately characterized. NHNs were classified into 1 of 2 categories, resolved or progressed, in which NHNs decreased by 2 mm or more in diameter without hypervascularity or increased by 2 mm or more or gained an arterial supply, respectively. A: In 58 progressed NHNs, 43% were detected in T1-weighted imaging (T1WI) and/or T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) (black box), whereas only 6.7% showed positive results in the resolved NHNs by T1WI and/or T2WI imaging, leading to a significantly higher detection rate among progressed NHNs; B: In the arterial phase, progressed NHNs were detected as less attenuated nodules (black box) with significantly higher frequency than resolved NHNs were (34.5% vs 6.7%, respectively, P = 0.05); C: The median patient age in the resolved NHN group was 51 years (IQR: 38-72 years), which was significantly younger than the 75 years (IQR: 70-77.3 years) of the progressed group; D: Serum albumin concentration was significantly higher in the resolved NHN group, 4.3 g/dL (IQR: 3.6-4.3 g/dL), than in the progressed group, 3.7 g/dL (IQR: 3.3-3.9 g/dL).
- Citation: Kanefuji T, Takano T, Suda T, Akazawa K, Yokoo T, Kamimura H, Kamimura K, Tsuchiya A, Takamura M, Kawai H, Yamagiwa S, Aoyama H, Nomoto M, Terai S. Factors predicting aggressiveness of non-hypervascular hepatic nodules detected on hepatobiliary phase of gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylene-triamine-pentaacetic-acid magnetic resonance imaging. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(15): 4583-4591
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i15/4583.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i15.4583