Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2014; 20(35): 12551-12558
Published online Sep 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i35.12551
Published online Sep 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i35.12551
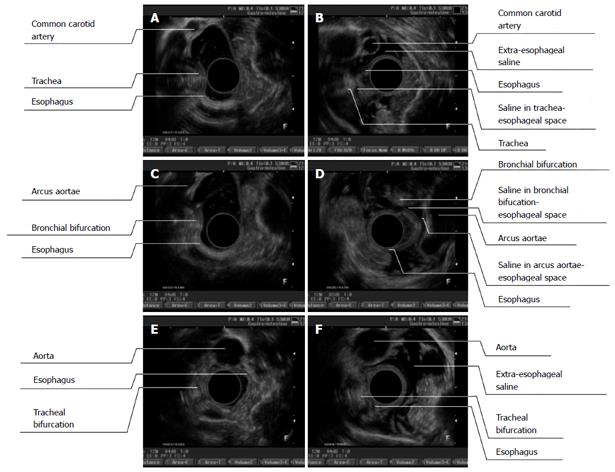
Figure 4 Endoscopic ultrasonography images (before and after endoscopic ultrasound) of different segments of the esophagus (A/B, upper thoracic segment; C/D, middle thoracic segment; E/F, lower thoracic segment).
A: Before extraesophageal saline injection (ESI), it was difficult to observe the esophageal adventitia and common carotid artery. The esophagus and trachea were observed to be close to each other, it was difficult to distinguish their boundaries, and the tracheal trace was distinct; B: After ESI, the space between the esophagus and the aorta along the left anterior wall was enlarged and displayed as a hypoechoic area. The esophageal adventitia and aortic adventitia were clearly distinguishable. A thread-like hypoechoic area was visualized between the esophageal-tracheal spaces, which created a clear boundary between them; C: Before ESI, it was difficult to distinguish between the adventitias of the esophagus and the arcus aortae; D: After ESI, the space between the esophagus and the arcus aortae was enlarged and filled with a hypoechoic area. The esophageal adventitia and aortic adventitia were clearly distinguishable; E: Before ESI, it was difficult to distinguish between the esophageal adventitia and the thoracic aorta; F: After ESI, the space between the esophagus and the thoracic aorta was enlarged and full of hypoechoic areas, and the adventitious of both the esophagus and the thoracic aorta were distinguishable.
- Citation: Li JJ, Shan HB, He LJ, Wang TD, Xiong H, Chen LM, Li XH, Huang XX, Luo GY, Li Y, Xu GL. Extraesophageal saline enhances endoscopic ultrasonography to differentiate esophagus and adjacent organs. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(35): 12551-12558
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i35/12551.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i35.12551