Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2014; 20(27): 9090-9097
Published online Jul 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.9090
Published online Jul 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.9090
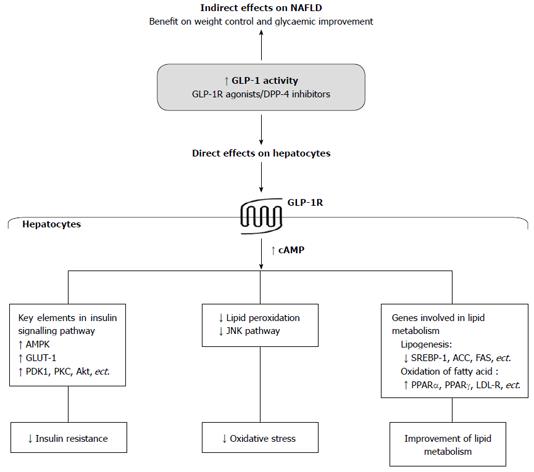
Figure 1 Potential mechanistic roles of Glucagon-like peptide-1 and Glucagon-like peptide-1-based therapies in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide-1; GLP-1R: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; DPP-4: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; cAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; PDK-1: Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase-1; PKC: Protein kinase C; Akt: Protein kinase B; GLUT-1: Glucose transporter-1; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase; SREBP-1: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1; ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; FAS: Fatty acid synthase; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator activator receptor; LDL-R: Low-density lipoprotein receptor.
- Citation: Liu Y, Wei R, Hong TP. Potential roles of glucagon-like peptide-1-based therapies in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(27): 9090-9097
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i27/9090.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.9090