Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2014; 20(24): 7914-7925
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7914
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7914
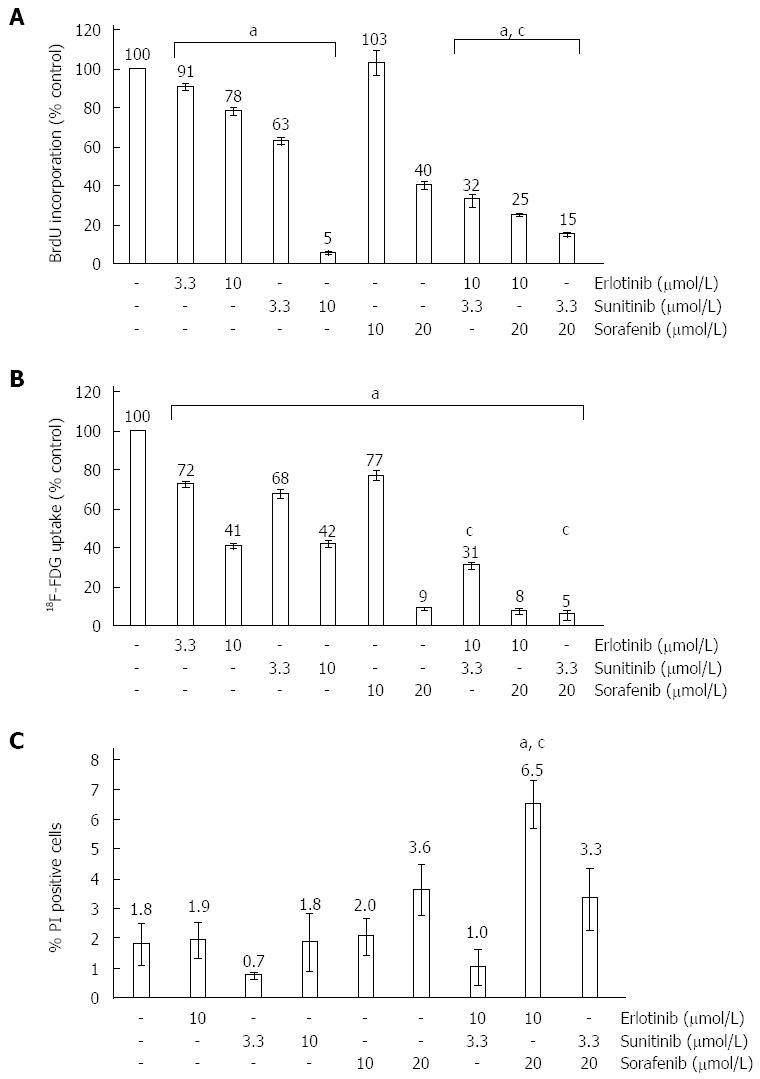
Figure 1 Effects of small molecule kinase inhibitors on DNA synthesis, 2-Deoxy-2-[18F] fluoroglucose uptake and survival of pancreatic stellate cells.
Pancreatic stellate cells (PSC) growing in primary culture were harvested, replated at equal seeding densities and treated with erlotinib, sunitinib, sorafenib and combinations thereof at the indicated concentrations for 24 h. Control cultures were exposed to the solvent DMSO only. A: The pretreated cells were labelled with 5-bromo-2’-deoxyuridine (BrdU) for another 24 h and proliferation was assessed with the BrdU DNA incorporation assay. One hundred percent BrdU incorporation corresponds to solvent-treated PSC. Data from n≥ 17 separate cultures per data point were used to calculate mean ± SE; B: The cells were labelled with 2-Deoxy-2-[18F] fluoroglucose (18F-FDG), and uptake quantified as described in the “Materials and methods” section. One hundred percent 18F-FDG uptake corresponds to solvent-treated PSC (n≥ 6; mean ± SE); C: Incubation was continued for another 24 h. Afterwards, the samples were subjected to a cytofluorometric quantification of dead [phosphatidylinositol (PI)-positive] cells, which are expressed as percent of the total cell number (n≥ 5; mean ± SE). (A-C) aP < 0.05, cP < 0.05 vs cultures treated with either of the two combined substances alone.
- Citation: Elsner A, Lange F, Fitzner B, Heuschkel M, Krause BJ, Jaster R. Distinct antifibrogenic effects of erlotinib, sunitinib and sorafenib on rat pancreatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(24): 7914-7925
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i24/7914.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7914