Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2014; 20(24): 7878-7886
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7878
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7878
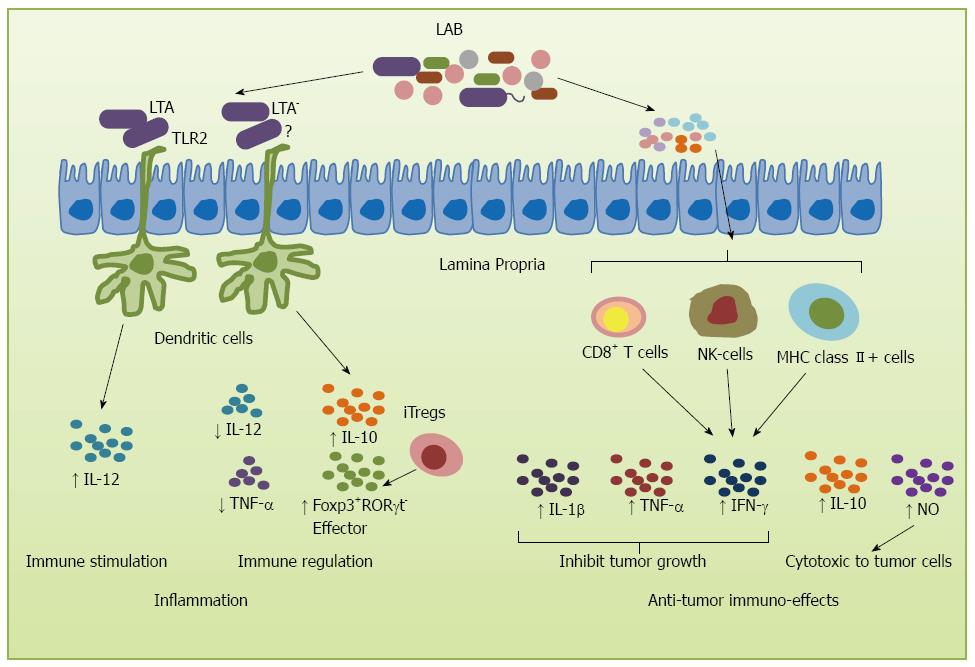
Figure 2 Immune responses induced by lactic acid bacteria.
Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) can provoke immune responses via two main pathways: inflammation and anticancer immune response. The inflammation pathways involve lipoteichoic acid (LTA) which can stimulate T cells to release interleukin (IL)-10, IL-12 and increase effectors Foxp3+RORγt- Tregs. In the anticancer immune response pathway, LAB stimulate the immune cells, such as T cells, dendritic cell (DC), natural killer (NK) and MHC class II cells to induce IL-10, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interferon (IFN)-γ and IL-1β to inhibit tumor growth.
- Citation: Zhong L, Zhang X, Covasa M. Emerging roles of lactic acid bacteria in protection against colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(24): 7878-7886
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i24/7878.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7878