Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2014; 20(20): 6180-6200
Published online May 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6180
Published online May 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6180
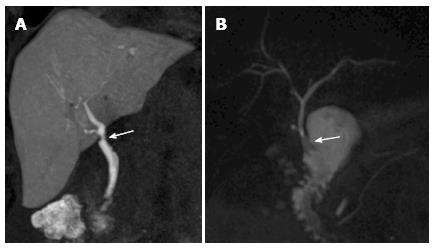
Figure 4 Biliary anatomy after liver transplant on magnetic resonance cholangiography images.
A: End-to-end anastomosis (arrow) between the donor common bile duct and the recipient common hepatic duct, as shown in this coronal T1-weighted magnetic resonance cholangiography (MRC) obtained after iv administration of an hepatobiliary contrast agent (gadoxetic acid); B: In the case of technical challenge, re-transplantation or primary sclerosing cholangitis as the cause of the transplant, choledochojejunostomy using a Roux-en-Y anastomosis (arrow) is performed, as shown in this maximum intensity projection reconstruction from a T2-weighted, 3D MRC examination.
- Citation: Girometti R, Como G, Bazzocchi M, Zuiani C. Post-operative imaging in liver transplantation: State-of-the-art and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(20): 6180-6200
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i20/6180.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6180