Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2014; 20(16): 4648-4661
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4648
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4648
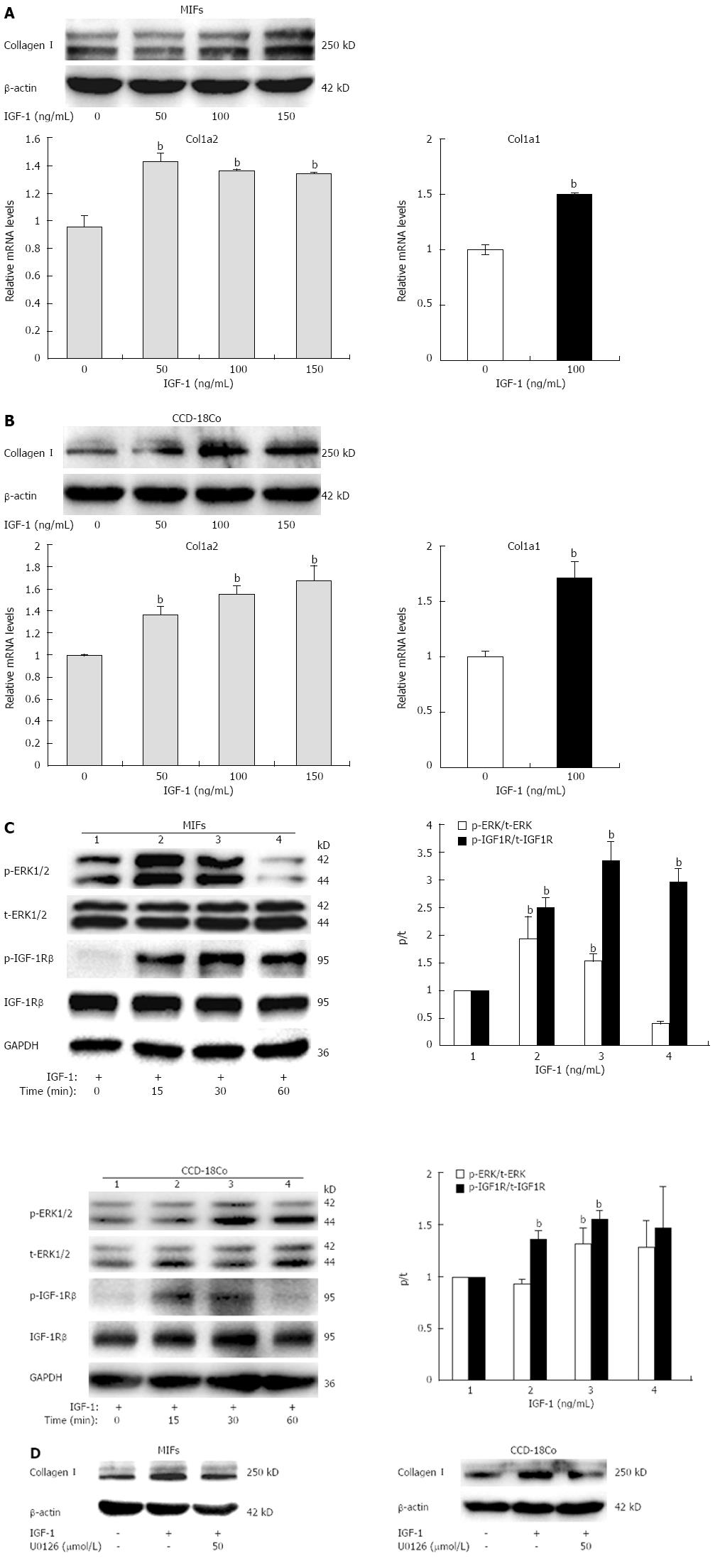
Figure 2 Insulin growth factor-1 induces collagen I expression via mitogen-activated protein-kinase pathway.
A, B: Collagen I protein and col1a2, col1a1 mRNA expression in mouse intestinal fibroblasts (MIFs) and CCD-18Co cells stimulated with increasing concentrations of insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1) for 24 h; C: Phosphorylation of IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R) (p-IGF-1R) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) (p-ERK1/2) in MIFs and CCD-18Co exposed to 100 ng/mL IGF-1 for 0, 15, 30, or 60 min. The bar graph represents the quantitation of the Western blotting normalized to the control; D: Cells were pretreated with 50 μmol/L mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase (MEK)/ERK inhibitor U0126 or vehicle for 1 h and then coincubated with 100 ng/mL IGF-1 for 24 h. Collagen I protein level was measured. The experiment was repeated three times and obtained similar results. Values represent mean ± SD. bP < 0.01 vs no treatment group. GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Li P, Liang ML, Zhu Y, Gong YY, Wang Y, Heng D, Lin L. Resveratrol inhibits collagen I synthesis by suppressing IGF-1R activation in intestinal fibroblasts. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(16): 4648-4661
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i16/4648.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4648