Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2014; 20(1): 22-30
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.22
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.22
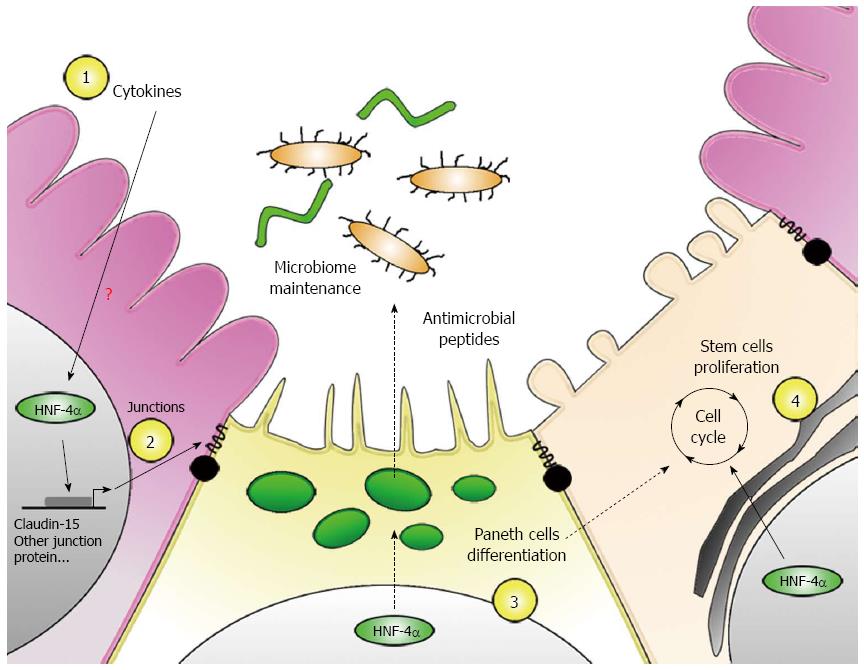
Figure 3 Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha potential physiological roles in protecting the gut against inflammation.
There are several hypotheses for the functional roles of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha (HNF4-α) in the context of intestinal inflammation. As observed in hepatocytes, intestinal epithelial HNF4-α could sense and regulate cytokines effect on gene transcription (1). Among others, HNF4-α could influence mucosal barrier properties by regulating the expression of cell junction proteins such as claudin-15 (2). Moreover, HNF4-α could influence microbiota homeostasis through its role on Paneth cells differentiation (3) and goblet cells mucins expression (not shown). Finally, HNF4-α could also be implicated in the maintenance of the regenerative properties of the mucosal barrier. It could participate to stem cells proliferation through maintaining Paneth cells differentiation and through indirect regulation of the β-catenin pathway (4).
- Citation: Babeu JP, Boudreau F. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha involvement in liver and intestinal inflammatory networks. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(1): 22-30
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i1/22.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.22