Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2014; 20(1): 163-174
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.163
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.163
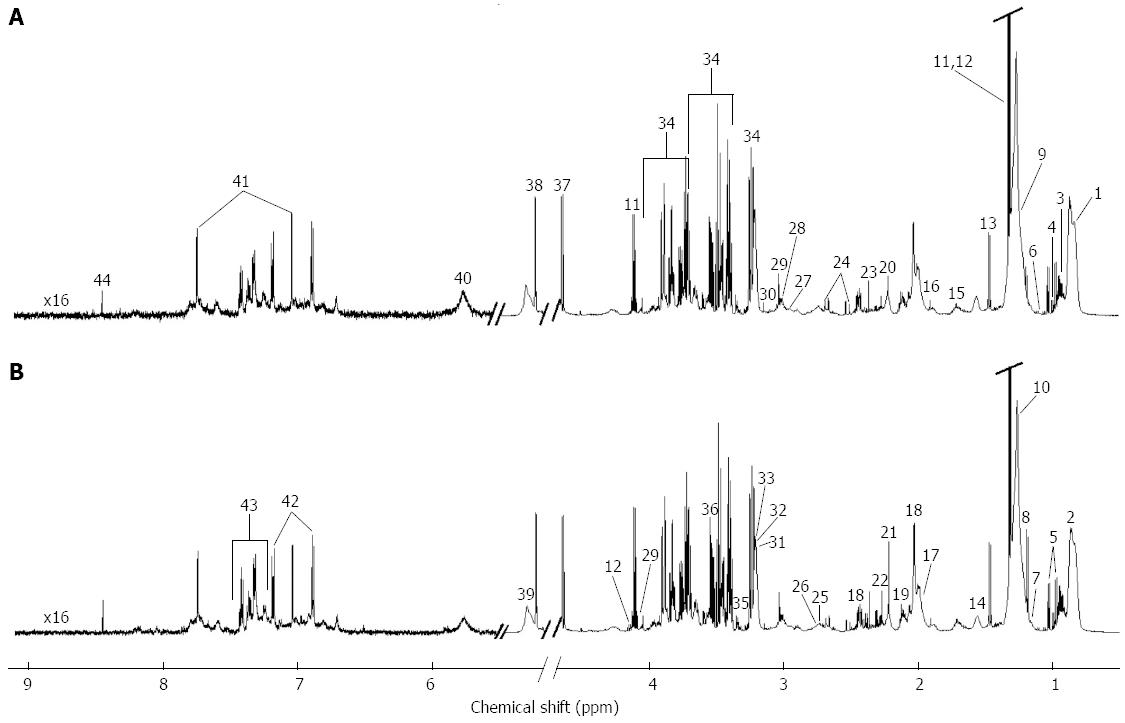
Figure 1 Median 600 MHz proton nuclear magnetic resonance noesy spectra of serum samples.
A: Healthy control subjects; B: Patients with inflammatory bowel diseases. 1: Lipids LDL CH3-(CH2)n-; 2: Lipids VLDL CH3-(CH2)n-; 3: Leucine; 4: Isoleucine; 5: Valine; 6: 3-Methyl-2-oxovalerate; 7: Isobutyrate; 8: 3-Hydroxybutyrate; 9: Lipids LDL CH3-(CH2)n-; 10: Lipids VLDL CH3-(CH2)n-; 11: Lactate; 12: Threonine; 13: Alanine; 14: Lipids VLDL CH2-CH2-C=O; 15: Lysine; 16: Acetate; 17: Lipids -CH2-CH=CH-; 18: N-acetylated compounds; 19: Glutamine; 20: Lipids -CH2-C=O; 21: Acetone; 22: Acetoacetate; 23: Pyruvate; 24: Citrate; 25: Dimethylamine; 26: Lipids =CH-CH2-CH=; 27: Trimethylamine; 28: Creatine; 29: Creatinine; 30: Dimethyl sulfone; 31: Choline; 32: Phosphocholine; 33: Glycerophosphocholine; 34: α and β-Glucose; 35: Methanol; 36: Glycine; 37: β-Glucose; 38: α-Glucose; 39: Lipids -CH=CH-; 40: Urea; 41: Tyrosine; 42: 1-Methylhistidine; 43: Phenylalanine; 44: Formate.
- Citation: Dawiskiba T, Deja S, Mulak A, Ząbek A, Jawień E, Pawełka D, Banasik M, Mastalerz-Migas A, Balcerzak W, Kaliszewski K, Skóra J, Barć P, Korta K, Pormańczuk K, Szyber P, Litarski A, Młynarz P. Serum and urine metabolomic fingerprinting in diagnostics of inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(1): 163-174
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i1/163.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.163