Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2013; 19(42): 7480-7486
Published online Nov 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7480
Published online Nov 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7480
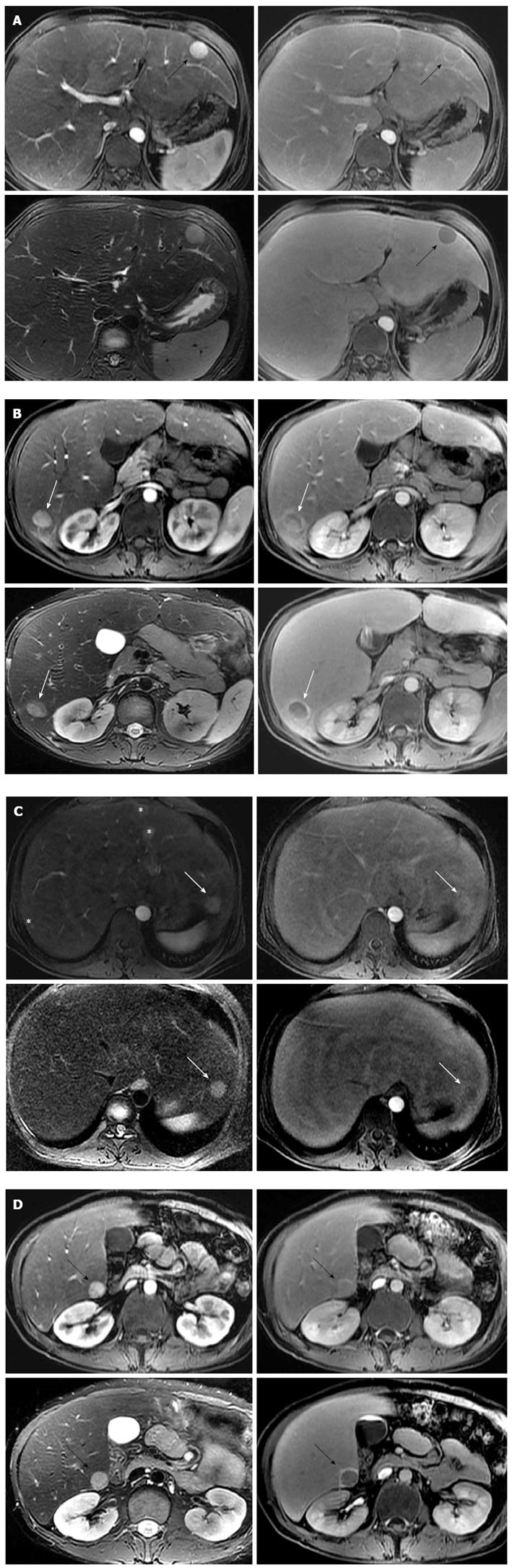
Figure 1 Hepatic adenomas associated with glycogen storage disease type Ia.
A: Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced axial T1-weighted image on arterial phase (left upper) reveals approximately 2 cm intense enhancing mass in the segment 3 of liver (black arrows). The mass shows nearly iso-signal intensity with capsular enhancement on 3 min delayed phase (right upper), intermediate high signal intensity on axial T2-weighted image (left lower), and clear defect on 20 min hepatobiliary phase (right lower); B: Approximately 1.8 cm sized intense enhancing mass on arterial phase (left upper) is noted in the segment 6 of liver. This mass shows suspicious focal eccentric wash-out enhancement (white arrows) on 3 min delayed phase (right upper). This portion reveals relatively low signal intensity on axial T2-weighted image (left lower) and 20 min hepatobiliary phase (right lower), compared to other tumor area. Surrounding rim enhancement in the tumor is seen on 20 min hepatobiliary phase; C: Approximately 1.8 cm arterial enhancing mass (white arrows) is seen in the segment 2 of liver. The mass reveals slightly high signal intensity on 3 min delayed phase (right upper), intermediate high signal intensity on axial T2-weighted image (left lower), and fuzzy defect on 20 min hepatobiliary phase (right lower). Multifocal arterioportal shunts (asterisks) are noted in the segments 3 and 7 of liver; D: Approximately 1.8 cm sized intense enhancing mass (black arrows) on arterial phase (left upper) is noted in the segment 6 of liver. This mass shows slightly high signal intensity with capsular enhancement on 3min delayed phase (right upper), and intermediate high signal intensity on axial T2-weighted image (left lower). On 20 min hepatobiliary phase (right lower), the tumor reveals clear defect with surrounding rim enhancement. Gd-EOB-DTPA: Gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid.
- Citation: Ahn SY, Park SY, Kweon YO, Tak WY, Bae HI, Cho SH. Successful treatment of multiple hepatocellular adenomas with percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(42): 7480-7486
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i42/7480.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7480