Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2013; 19(4): 492-502
Published online Jan 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i4.492
Published online Jan 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i4.492
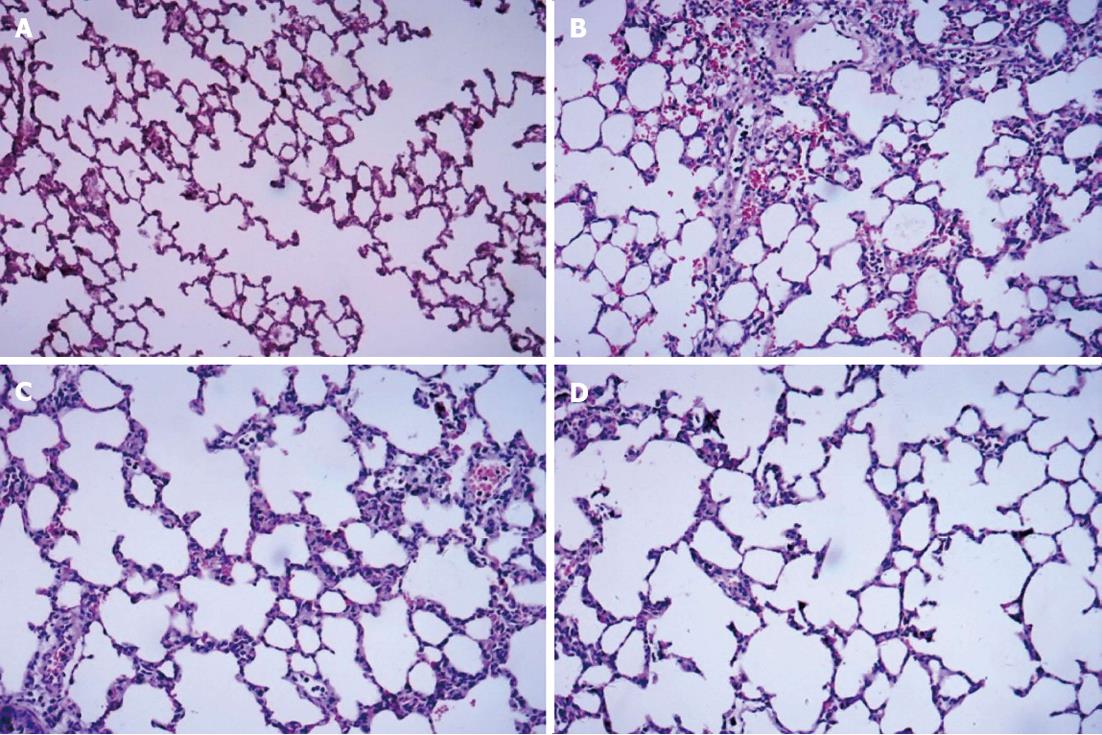
Figure 1 Hematoxylin and eosin staining of dorsal lobe of right lung tissue.
A: Control group; B: Septic shock group; C: The early fluid resuscitation-treated group; D: Combined early fluid resuscitation and 2% hydrogen inhalation-treated group. Lung tissues were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for more than 24 h. After dehydrating and embedding, they were cut into 5 μm slices, and were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. The pathogenesis of lung injury was observed under a microscope (original magnification × 200). Normal alveolar structure was found in Group A. In Group B, disorders of the alveolar structures, severe neutrophil infiltration in the alveoli and alveolar capillary congestion were observed. In Group C, the extent of neutrophil accumulation and the alveolar-capillary exudate were reduced compared with Group B. However, significant decreases in alveolar damage were found in Group D, and there was significant improvement in alveolar edema compared with Group C.
- Citation: Liu W, Shan LP, Dong XS, Liu XW, Ma T, Liu Z. Combined early fluid resuscitation and hydrogen inhalation attenuates lung and intestine injury. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(4): 492-502
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i4/492.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i4.492