Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2013; 19(36): 6044-6054
Published online Sep 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i36.6044
Published online Sep 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i36.6044
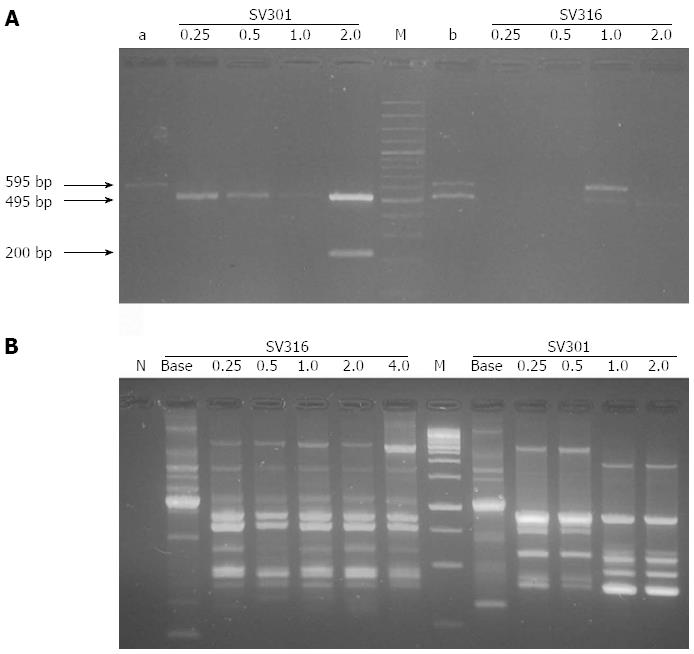
Figure 1 Electrophoretic analysis.
A: EPIYA polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products from DNA of the Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) isolates SV301 and SV316 that grew in the Amoxicillin serial dilutions, the PCR products were analyzed in agarose gel at 2%. Lines a and b positive controls; line a: Clinical H. pylori isolate (PZ5085) with EPIYA ABCC motif (570 ± 25 bp) confirmed by sequencing; Line b: A mix of DNA from isolate PZ5085 and from the H. pylori strain 26695 with EPIYA-ABC motif (470 ± 25 bp). M: 100 bp DNA ladder. Distribution of different molecular weights among isolates is an indication of the presence of multiple EPIYA repetitions; B: Random amplified polymorphic DNA fingerprints generated with primer 1254 in H. pylori isolates resistant in baseline (without antibiotic pressure) and resistant isolates growing in each of the serial antibiotic dilutions (with antibiotic pressure); line N: negative reaction control; M: 100 bp ladder.
-
Citation: Bustamante-Rengifo JA, Matta AJ, Pazos A, Bravo LE.
In vitro effect of amoxicillin and clarithromycin on the 3’ region ofcagA gene inHelicobacter pylori isolates. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(36): 6044-6054 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i36/6044.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i36.6044