Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2013; 19(30): 4907-4916
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4907
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4907
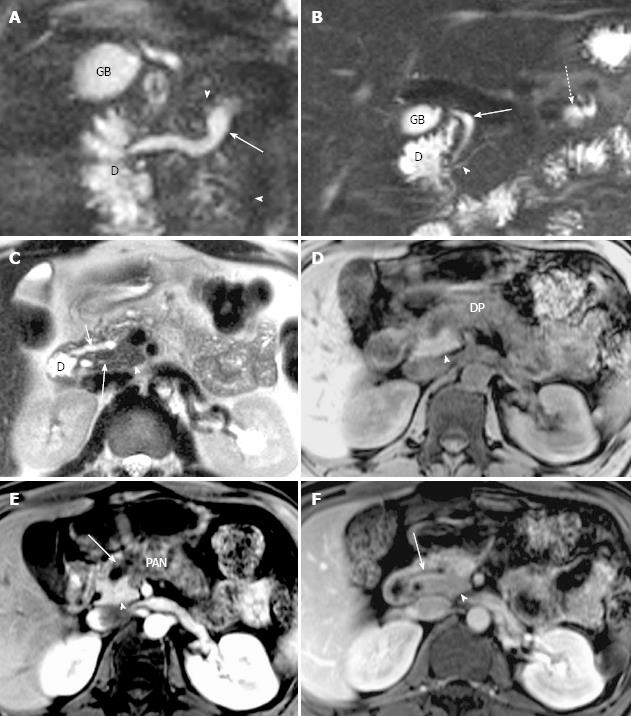
Figure 4 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography and magnetic resonance imaging of recurrent acute pancreatitis only involving the dorsal pancreas in a 43-year-old man.
A: Coronal-oblique, thin-section half-Fourier rapid acquisition with relaxation enhancement magnetic resonance (RARE-MR) cholangiogram [infinite/95 (effective), 3-mm section thickness] shows marked dilatation (1 cm in diameter) of duct of Santorini (arrow) with apparent side branch ectasia (arrowheads). The gallbladder (GB) and the duodenum (D) are demonstrated clearly; B: Coronal-oblique, thin-section half-Fourier RARE MR cholangiogram [infinite/95 (effective), 3-mm section thickness] shows normal common bile duct (arrow) and ventral duct (arrowhead) of pancreas. The cystic changes secondary to pancreatitis in the pancreatic tail (dotted arrow) is shown while the GB and duodenum (D) appear normal; C: Axial T2WI shows dilatation and irregularity of duct of Santorini (short arrow) which enters the duodenum (D) via minor papilla. The ventral duct (solid arrow) and the pancreatic uncinate (arrowhead) are normal in size and signal intensity while the anterior portion of pancreatic head is abnormal with elevation of signal intensity; D: Axial precontrast T1WI SPGR shows that the pancreatic uncinate (arrowhead) is normal in size and signal intensity and the dorsal pancreas (DP) is abnormal with decreased T1 signal intensity and the swelling of the parenchyma; E: Axial T1WI SPGR after administration of Gd-DTPA at arterial phase shows normal enhancement of the pancreatic uncinate (arrowhead) and the enhancement of dorsal pancreas (PAN) is remarkably compromised with duct dilatation (arrow) and cystic changes; F: Axial T1WI SPGR at portal venous phase after administration of Gd-DTPA shows normal wash-out of contrast material in pancreatic uncinate (arrowhead) and delayed enhancement of the anterior portion of pancreatic head with dilatation of duct of Santorini (arrow).
- Citation: Wang DB, Yu J, Fulcher AS, Turner MA. Pancreatitis in patients with pancreas divisum: Imaging features at MRI and MRCP. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(30): 4907-4916
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i30/4907.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4907