Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2013; 19(28): 4475-4485
Published online Jul 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4475
Published online Jul 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4475
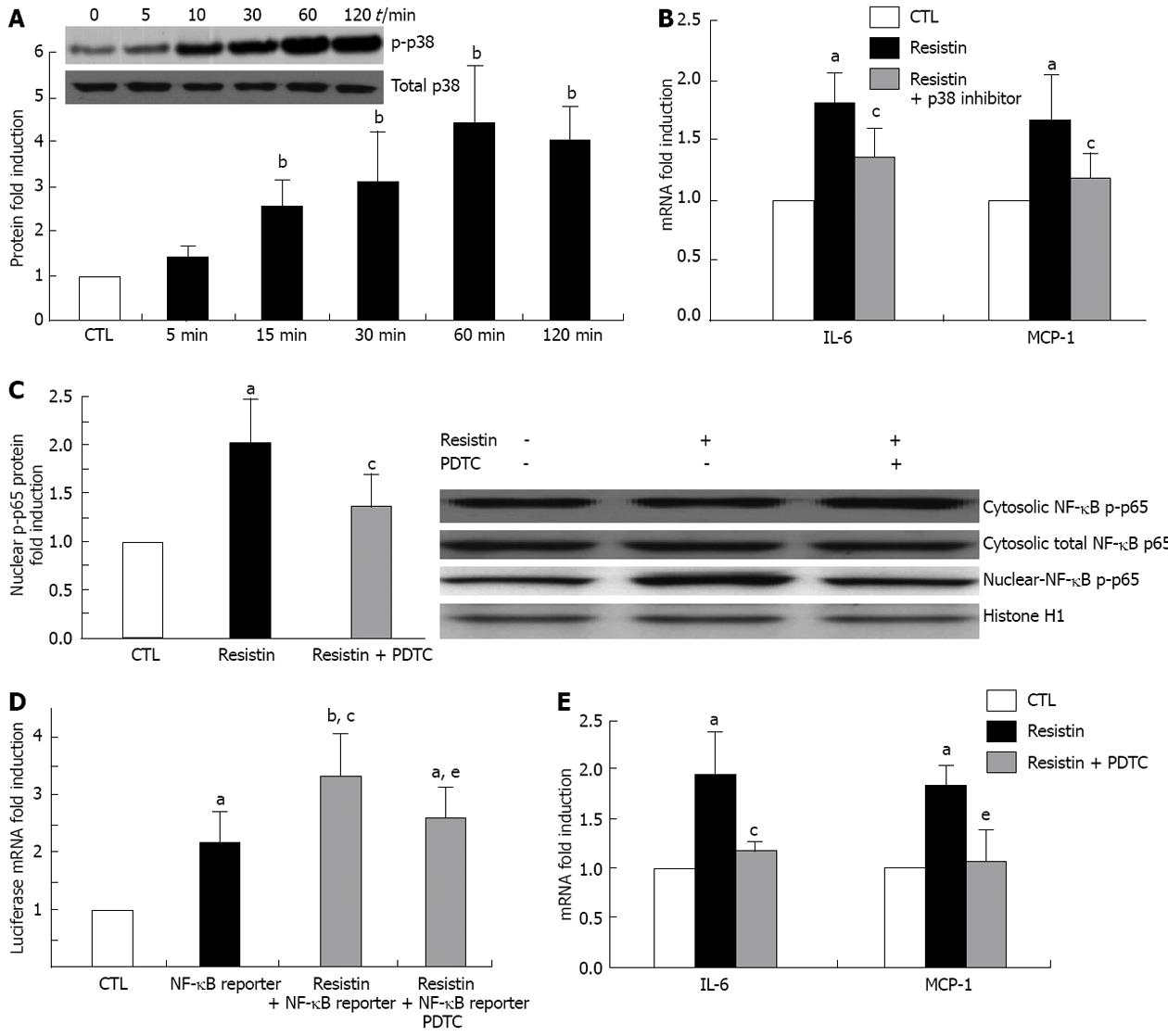
Figure 4 Resistin activates hepatic stellate cells MAPK/p38 and nuclear factor κB p65.
Rat hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) at day 4 were cultured with resistin (500 ng/mL) for 120 min. Cytosolic and nuclear proteins were extracted and Immunoblot performed to quantify p-p38 and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) p-p65. For NF-κB DNA binding capacity, 3 × NF-κB /Luc reporter was added to the culture for 24 h and Luciferase mRNA quantified by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. For the p-p38 and NF-κB inhibition experiments, SB203580 (20 μmol/L, p-p38 inhibitor) or pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC) (100 μmol/L, NF-κB inhibitor) was added 1 h before resistin treatment. Resistin (500 ng/mL) was added to rat HSCs for 24 h. A: p-p38 was enhanced by resistin; B: p-p38 inhibition (24 h) diminished resistin-induced interleukin 6 (IL-6) and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) increase by HSCs; C: Nuclear p-p65 was increased by resistin exposure and decreased by PDTC (120 min); D: Luciferase mRNA was augmented by resistin and diminished by PDTC (24 h); E: PDTC reversed resistin-induced enhancement of IL-1 and MCP-1 (24 h). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. At least three independent experiments were conducted in triplicate for data analysis. aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs controls (untreated); cP < 0.05 vs resistin treatment alone or NF-κB reporter treatment alone; eP < 0.05 vs combination of resistin and NF-κB reporter.
- Citation: Dong ZX, Su L, Brymora J, Bird C, Xie Q, George J, Wang JH. Resistin mediates the hepatic stellate cell phenotype. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(28): 4475-4485
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i28/4475.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i28.4475