Published online Jul 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i26.4200
Revised: March 22, 2013
Accepted: April 27, 2013
Published online: July 14, 2013
AIM: To investigate the metabolic profiles of xenograft pancreatic cancer before and after radiotherapy by high-resolution magic angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (HRMAS 1H NMR) combined with principal components analysis (PCA) and evaluate the radiotherapeutic effect.
METHODS: The nude mouse xenograft model of human pancreatic cancer was established by injecting human pancreatic cancer cell SW1990 subcutaneously into the nude mice. When the tumors volume reached 800 mm3, the mice received various radiation doses. Two weeks later, tumor tissue sections were prepared for running the NMR measurements. 1H NMR and PCA were used to determine the changes in the metabolic profiles of tumor tissues after radiotherapy. Metabolic profiles of normal pancreas, pancreatic tumor tissues, and radiation- treated pancreatic tumor tissues were compared.
RESULTS: Compared with 1H NMR spectra of the normal nude mouse pancreas, the levels of choline, taurine, alanine, isoleucine, leucine, valine, lactate, and glutamic acid of the pancreatic cancer group were increased, whereas an opposite trend for phosphocholine, glycerophosphocholine, and betaine was observed. The ratio of phosphocholine to creatine, and glycerophosphocholine to creatine showed noticeable decrease in the pancreatic cancer group. After further evaluation of the tissue metabolic profile after treatment with three different radiation doses, no significant change in metabolites was observed in the 1H NMR spectra, while the inhibition of tumor growth was in proportion to the radiation doses. However, PCA results showed that the levels of choline and betaine were decreased with the increased radiation dose, and conversely, the level of acetic acid was dramatically increased.
CONCLUSION: The combined methods were demonstrated to have the potential for allowing early diagnosis and assessment of pancreatic cancer response to radiotherapy.
Core tip: In the present study, for the first time to our knowledge, high-resolution magic angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy and principal components analysis were combined to highlight metabolite profiles of pancreatic cancer after radiotherapy, by analyzing the correlation between radiotherapy effect and metabolic change, and optimizing the therapeutic scheme. The results showed that metabolic profile changes of pancreatic cancer after radiotherapy were closely correlated with therapeutic effect. The outcome of the study is both interesting and beneficial to pathological research, early diagnosis, and therapy evaluation of pancreatic diseases.
- Citation: He XH, Li WT, Gu YJ, Yang BF, Deng HW, Yu YH, Peng WJ. Metabonomic studies of pancreatic cancer response to radiotherapy in a mouse xenograft model using magnetic resonance spectroscopy and principal components analysis. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(26): 4200-4208
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i26/4200.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i26.4200
Pancreatic cancer is a malignant tumor with very poor prognosis, and surgery has been considered as the only radical therapy. However, about 85% of newly diagnosed cases have developed distant metastasis, and only 5%-25% of pancreatic head cancer and less than 10% of pancreatic body cancer can be treated with surgical excision, and the postoperative recurrence rate is high. Therefore, radiation therapy has become the predominant treatment method for locally advanced pancreatic cancer[1-3]. Therapeutic evaluations of radiotherapy are mainly: remission from the symptoms of pain and jaundice, solid tumor size and its survival time, and the lack of a specific targeted method. During the last three decades, there has been ongoing magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) research in malignant diseases. These studies provided valuable data on the biochemistry and metabolism of tumors, and on the effects of nutrients, hormones, and growth factors[4,5]. The mechanisms of action of anticancer drugs and the acquired resistance to these agents were delineated[6,7]. MRS was also used for monitoring the response to therapy[8,9].
High-resolution magic angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (HRMAS 1H NMR) is a well-recognized technique in metabonomics studies in vitro, by which biopsy or postmortem samples of intact tissues are spun at the magic angle, resulting in a significant improvement in the resolution of the spectrum obtained for some of the line-broadening factors, such as dipole–dipole interactions and chemical shift anisotropy, and magnetic field inhomogeneities are averaged out[10,11]. This approach requires minimal sample preparation and, unlike convenient 1H NMR spectroscopy of tissue extracts, both aqueous and lipid-soluble metabolites can be observed simultaneously in situ. In addition, information about the metabolic environment of the tumor can also be obtained. Therefore, HRMAS 1H NMR has proved to be an efficient method for studying a wide variety of cancers, including breast cancer[12], cervical cancer[13], kidney cancer[14], prostate cancer[15], malignant lymph nodes[16], and liposarcoma[17] of animals and humans. However, so far, there are very few metabonomic studies in cancer therapeutics by the application of HRMAS 1H NMR.
HRMAS 1H NMR spectra obtained from tissues reflect the dynamic biological systems and processes that contribute to the overall metabolic status of an organism. It is not possible to isolate the effects of any single metabolite signal in a spectrum and, furthermore, the manual analysis of even a small number of such spectra is a laborious and complex task. Therefore, metabonomists utilize data reduction and multivariate analysis techniques, such as principal components analysis (PCA), to facilitate automated NMR pattern recognition[18,19]. Moreover, our previous study demonstrated that using 1H NMR and PCA could discriminate pancreatic cancer from chronic pancreatitis accurately[20]. In the present study, HRMAS 1H NMR and PCA were combined to highlight metabolite profiles of pancreatic cancer after radiotherapy, in order to analyze the correlation between radiotherapy effects and metabolic changes, and to optimize the therapeutic scheme. The study has an important implication for reference guides on therapeutic evaluation by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy on pancreatic cancer in vivo.
Six- to eight-week-old female nude mice were obtained from the Planned Parenthood Research Institute, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China. All animals in this study were housed under pathogen-free conditions and maintained in accordance with the guidelines of the Committee on Animals of the Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, China. Human pancreatic cancer cell line SW1990 in mid-log-growth phase was harvested by trypsinization. Single-cell suspensions (5 × 106 cells in 0.1 mL HBSS) were injected subcutaneously into the nude mice. The tumors were measured every 4 d with a caliper, and the diameters were recorded. Tumor volume was calculated by the formula: a2b/2, where a and b are the two maximum diameters. When tumors reached 2.0 cm × 2.0 cm, the duration of survival was recorded and the mouse euthanized.
For the radiotherapy experiment, when the tumor volume reached 800 mm3, the mice were divided into four groups. Group A mice were used as untreated controls. Groups B, C, and D received 10, 20, and 30 Gy radiation doses, respectively. Tumor size was measured as described above. Two weeks later, tumor tissue sections were prepared for histological tests or for running the NMR measurements.
HRMAS 1H NMR experiments were carried out using a DRX-500 spectrometer (1H frequency at 500.13 MHz; Bruker Biospin, Rheinstetten, Germany). Tissue samples were rinsed three times with D2O and placed into a 4-mm zirconium oxide MAS rotor with drops of D2O (deuterium lock reference). Spectra were acquired at 300.0 K using single-pulse and CPMG pulse sequences, both with water presaturation during the relaxation delay of 2 s. CPMG pulse sequence was applied as a T2 filter to suppress signals from the molecules with short T2 values (such as macromolecules and lipids) using a total TE of 320 ms. The main parameters used for 1H NMR spectra were: SW = 15 kHz; TD = 64 k; NS = 256; and MAS rate = 5 kHz. Spectral assignments were confirmed by 2-dimensional 1H-1H TOCSY and 1H-1H COSY (data not shown), together with values obtained from the literature[10,21].
The stability of tissue samples was evaluated by repeating a 1-dimensional NMR experiment after overall acquisition. No biochemical degradation was observed for any of the tissue samples.
Spectral data were phased and baseline-corrected using XWINNMR (Bruker Biospin). All FID were multiplied by an exponential function equivalent to a 0.3-Hz line broadening factor prior to Fourier transformation. Each HRMAS 1H NMR spectrum was segmented into 211 regions of equal width (0.04 ppm) over the region 0.00-10.00, and the signal intensity in each region was integrated using AMIX version 3.6 (Bruker, Biospin). The region 4.50-5.00 was removed to eliminate baseline effects of imperfect water saturation. Prior to PCA, each integral region was normalized by dividing by the sum of all integral regions for each spectrum[12,14]. In order to exclude the effects of lipids and concentrate on the impacts of LMW metabolites in the CCM region, PCA was again done for 1H CPMG NMR spectra over the range 0.7-4.70, each 0.04 ppm wide. PCA was used to calculate a new, smaller set of orthogonal variables from linear combinations of the intensity variables, while retaining the maximum variability present within the data. These new variables are the derived principal components, and the distribution of their values (scores) permits the simple visualization of separation or clustering between samples. The weightings (loadings) given to each integral region in calculating the principal components allows for the identification of those spectral regions of greatest influence to the separation and clustering and, hence, the deduction of biomarkers of pancreatic cancer.
Continuous variables are expressed as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis of data was done by Student’s t test using SigmaPlot software. Differences were considered statistically significant at P < 0.05.
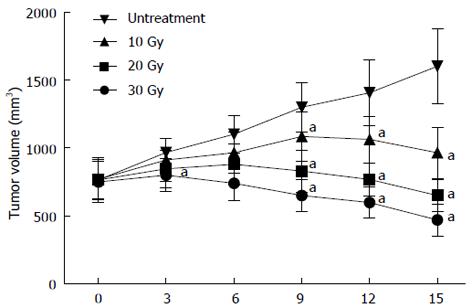
One week after SW1990 tumor cell inoculation, tumor size was measured and tumor volume recorded weekly. All 32 nude mouse models generated tumor tissues, and the success rate of model construction was 100% (32/32). Tumor volume in the control group (untreated), and the three groups which were given 10, 20, and 30 Gy radiation are shown in Figure 1. The transplanted tumor volume before treatment was 0.8 cm3 on average, increasing with breeding period in the control group. Compared with the control group, the tumor volume of the treatment groups reduced significantly, with the most obvious being the 30 Gy dose treatment group. These data showed that radiotherapy could effectively suppress the growth of pancreatic cancer in the nude mice. The changes in the morphological levels are expected to be accompanied with observable changes in the tissue biochemical composition which can be accessed with HRMAS 1H NMR spectroscopy ex vivo.
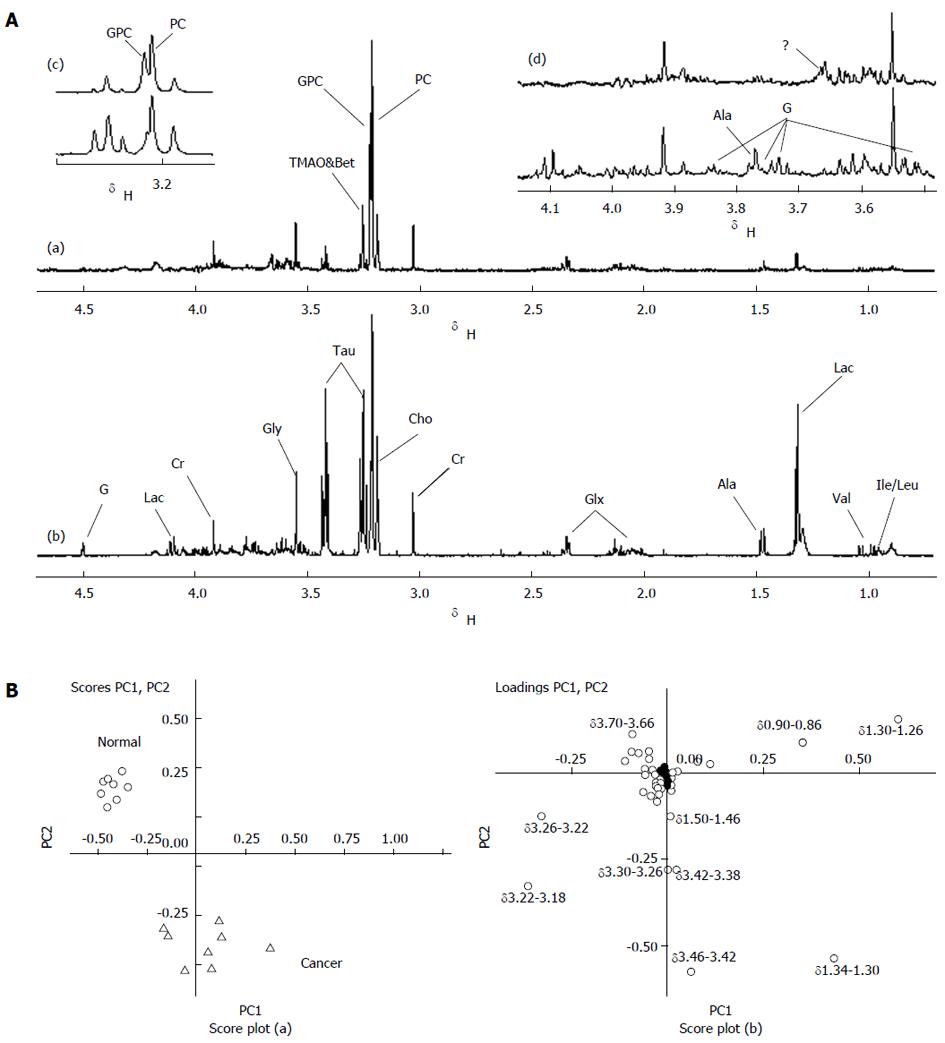
Using 1H NMR spectroscopy, components such as Cho, taurine (Tau), betaine (Bet), glutamic acid (Glu), glycerophosphocholine, and choline phosphate (GPC + PC), acetic acid (Ace), alanine (Ala), and lactic acid (Lac) were detected and identified in the normal pancreas and isolated transplanted tumor tissues in the nude mouse by their spectrum peaks. The literature was referred to before (18-20) and 2-D spectrum estimation (J-res, COSY, TOCSY) (Figure 2A). Score plots of PCA based on 1H NMR spectra were performed on 8 normal and 8 tumor samples, in which the spectra region was δ = 0.70-4.70, and the minimal region δ = 0.04 (Figure 2B). As shown in the loading plots, the main factors that differentiated the samples were δ 0.90-0.86, δ 1.34-1.26, δ 1.50-1.46, δ 3.30-3.18, δ 3.46-3.38, and δ 3.70-3.66, which were consistent with what was observed in Figure 2A, corresponding to the residual lipid, Lac, Ala, Cho compound, Tau, and unknown chemicals.
As is well-known, absolute concentration quantification for metabolites is difficult in HRMAS spectroscopy, and the metabolite ratios are commonly used for statistical analysis. Table 1 shows the relative signal integrals and signal ratios for some metabolites that contributed to the classification of normal pancreas and pancreatic tumor tissues discussed in the above sections. Compared to the normal pancreas, concentrations of Ileu, Leu, Val, Lac, Ala, Glu, Tau, Cho, and some carbohydrates (G, contained galactose β-H possibly due to characteristic twin peak at δ 4.52) increased relatively in the pancreatic tumor samples, while GPC + PC, Bet, GPC/Cre, and unknown chemicals at δ 3.66 decreased relatively. The level of Ace and PC/Cre showed no significant change.
| Normal pancreas | Pancreatic tumor | P-value | ||
| Metabolites | Choline | 2.75 ± 1.37 | 3.99 ± 0.35 | 0.0376 |
| Taurine | 1.99 ± 0.55 | 13.63 ± 2.92 | 0.0001 | |
| Betaine | 2.91 ± 0.57 | 1.58 ± 0.47 | 0.0002 | |
| Glutamic acid | 0.29 ± 0.11 | 0.46 ± 0.13 | 0.0260 | |
| Alanine | 0.60 ± 0.14 | 1.93 ± 0.16 | 0.0001 | |
| Lactate | 1.93 ± 0.86 | 8.30 ± 1.02 | 0.0001 | |
| Acetic acid | 0.06 ± 0.10 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.7942 | |
| Glycerophosphocholine+ phosphocholine | 19.47 ± 1.36 | 16.61 ± 1.31 | 0.0007 | |
| Metabolites ratio | Glycerophosphocholine/Creatine | 3.51 ± 0.76 | 2.35 ± 0.58 | 0.0042 |
| Phosphocholine/Creatine | 5.19 ± 0.96 | 6.22 ± 1.52 | 0.1284 |
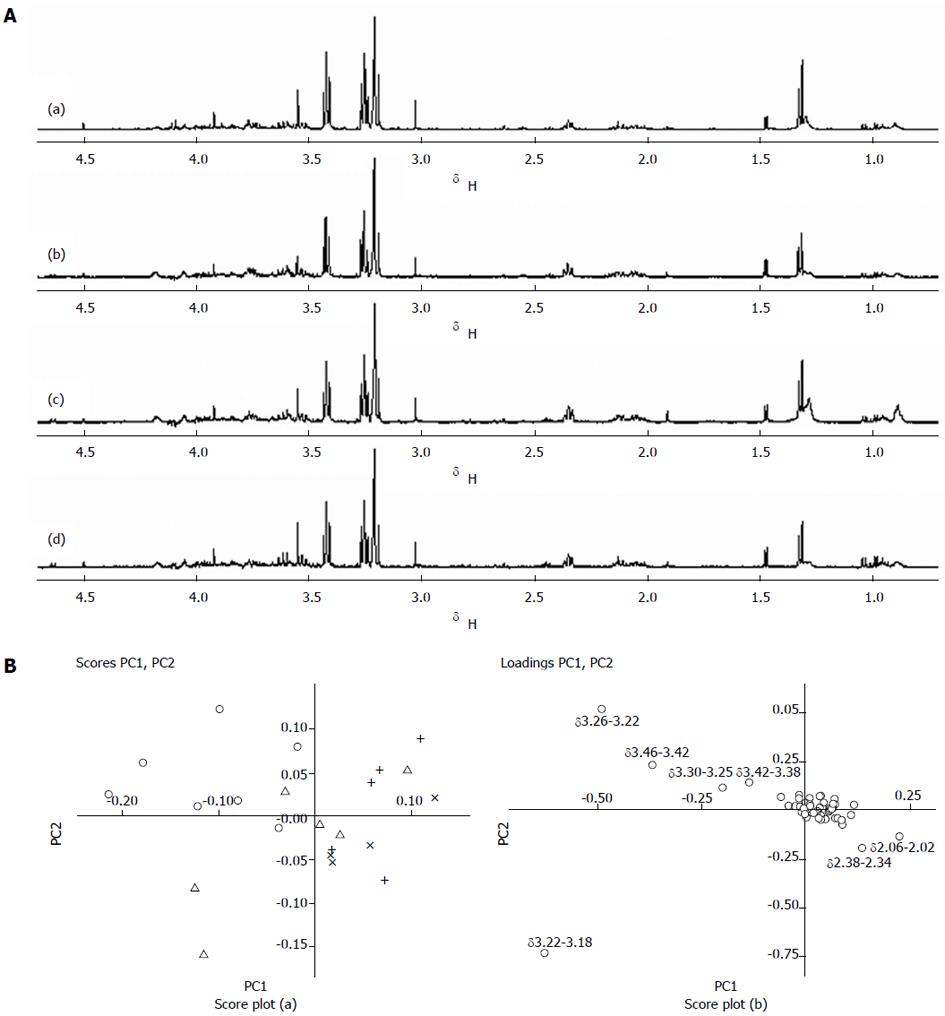
The metabolic profiles of tumor tissues after radiotherapy were also detected by 1H NMR. As shown in Figure 3A, no significant metabolic changes were observed in the 1H NMR spectrum. PCA analysis was further conducted on samples in each group, with the spectrum integration region δ = 0.70-4.70, and the minimal region δ = 0.04 (Figure 3B). In score plots, most of samples in the control group concentrate in the upper left, but overlap partly with samples in the 10 Gy radiation dose group. A partial overlap is shown between the 10, 20, and 30 Gy radiation dose groups, but overall it seems that the three groups have a left, upper, and lower distribution trend in terms of scores. Loading plots showed the changes of Cho-containing compounds, along with Ace and Bet content among the three dose groups.
Table 2 shows the relative signal integrals and signal ratios for some metabolites that contributed to the evaluation of pancreatic tumor tissues response radiotherapy. Cho content showed a significant difference between the control and 30 Gy dose groups, as well as the 10 and 30 Gy dose groups. The Cho content decreased with an increase of radiation dosage. Bet content also decreased with an increase of radiation dosage. In contrast, Ace content showed a positive relationship with the radiation dosage.
| Untreated | 10 Gy | 20 Gy | 30 Gy | P-value | ||
| Metabolites | Choline | 3.99 ± 0.35 | 3.97 ± 0.43 | 3.77 ± 0.36 | 3.44 ± 0.36 | 0.00751 |
| 0.37402 | ||||||
| 0.90123 | ||||||
| Taurine | 13.63 ± 2.92 | 13.43 ± 3.25 | 11.45 ± 2.20 | 12.41 ± 3.03 | 0.42621 | |
| 0.11412 | ||||||
| 0.90053 | ||||||
| Betaine | 1.58 ± 0.47 | 1.69 ± 0.38 | 1.23 ± 0.45 | 0.79 ± 0.30 | 0.00131 | |
| 0.14662 | ||||||
| 0.62753 | ||||||
| Glutamic acid | 0.46 ± 0.13 | 0.38 ± 0.07 | 0.43 ± 0.10 | 0.48 ± 0.17 | 0.84081 | |
| 0.64802 | ||||||
| 0.13663 | ||||||
| Alanine | 1.93 ± 0.16 | 2.10 ± 0.40 | 2.01 ± 0.27 | 1.96 ± 0.42 | 0.88181 | |
| 0.48212 | ||||||
| 0.28903 | ||||||
| Lactate | 8.30 ± 1.02 | 7.79 ± 1.43 | 7.51 ± 1.33 | 7.55 ± 0.85 | 0.13161 | |
| 0.20312 | ||||||
| 0.42593 | ||||||
| Acetic acid | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.15 ± 0.06 | 0.25 ± 0.07 | 0.27 ± 0.13 | 0.00251 | |
| 0.00012 | ||||||
| 0.00133 | ||||||
| Glycerophosphocholine + phosphocholine | 16.61 ± 1.31 | 19.95 ± 5.87 | 20.59 ± 5.79 | 20.80 ± 5.44 | 0.05221 | |
| 0.07832 | ||||||
| 0.13833 | ||||||
| Metabolites ratio | Glycerophosphocholine/Creatine | 2.35 ± 0.58 | 2.19 ± 0.15 | 2.49 ± 0.83 | 2.11 ± 0.36 | 0.33121 |
| 0.70872 | ||||||
| 0.44873 | ||||||
| Phosphocholine/Creatine | 6.22 ± 1.52 | 5.92 ± 0.44 | 5.87 ± 1.09 | 6.51 ± 1.28 | 0.68051 | |
| 0.60652 | ||||||
| 0.60963 |
Although HRMAS 1H NMR combined with PCA has been demonstrated as an efficient method for studying a wide variety of animal and human cancers[12-17], this combined method has not been reported to analyze the metabolic features of cancer response to therapy. Here, for the first time to our knowledge, our findings demonstrate that applying this combined method has the potential for clinical assessment of the pancreatic cancer radiotherapeutic response.
Kaplan et al[22] conducted 1H NMR analysis on perchlorate extract (water-soluble) of heterotopic transplanted pancreatic cancer tissue in nude mice. Compared with the normal pancreas of nude mice, Tau and Lac content in transplanted tumors increased, GPC content decreased, and there was little change in Cho and PC. However, in previous studies, some important information may be missed, and human factors introduced as a destructive process in extraction will lead to a negative impact on the results, along with poor experimental repeatability results from different pH values. Therefore, in this study, 1H NMR combined with PCA was applied to the metabolic study on transplanted tumor tissues in a human pancreatic tumor-bearing nude mouse model. This has avoided the error factor involved in complex processes such as tissue extraction. Moreover, due to the application of the 500 mHz high-field strength NMR instrument, the spectrum resolution obtained is significantly higher than that reported in the literature, with more metabolites being found and variation characteristics of metabolites embodied more clearly. Consequently, not only did the accuracy of spectrum peak identification improve, but statistical analysis errors were also reduced. In this study using 1H NMR combined with PCA, pancreatic cancer was shown to have higher Tau, Ileu, Leu, Val, Lac, Ala, Glu, and Cho levels relative to normal pancreas, while GPC + PC, and Bet and GPC/Cre levels decreased relatively. Compared to the other metabolites, Tau, Lac, and Ala had the most noticeable differences between normal pancreas and pancreatic cancer. Ace and PC/Cre showed no significant difference between normal and pathological conditions. The results suggest that these changes in the metabolite profile might be used as metabolic markers for the early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.
Radiotherapy is a local treatment, and its ultimate goal is to eradicate tumor cells thoroughly, while protecting normal tissues and vital organs as much as possible[23]. The application of computer tomography simulations and the three-dimensional conformal technique in radiotherapy has boosted the pancreatic target dosage and offered better protection for the gastrointestinal tract. Currently, therapeutic evaluations of radiotherapy are mainly: remission from the symptoms of pain and jaundice, solid tumor size and its survival time, and the lack of a specific targeted method[23]. By imaging examination, tumor size and contrast agent enhancement were observed to determine tumor activity, and indirectly determine therapy efficacy, although lacking strong direct evidence[24-27]. In this study, we use 1H NMR and PCA to compare pancreatic cancer metabolic variation characteristics before and after radiotherapy. Although no significant metabolic changes were observed in the 1H NMR spectra, PCA results showed a trend of certain changes among different dosage groups. We found that the Ace level was increased, which positively correlated with the radiation dose. In contrast, Cho and Bet levels were decreased, which inversely correlated with the radiation dose. Additionally, other metabolites, including Tau, Ileu, Leu, Val, Lac, Ala, Glu, and GPC + PC showed no significant change after radiotherapy. Thus, these data suggest that the changes in these metabolite profiles might provide a reference guide on therapeutic evaluation by NMR on pancreatic cancer in vivo.
Choline-containing metabolites (CCM) have already been chosen as biomarkers in various carcinoma studies[28,29]; however, they have not been mentioned in cancer treatment so far. CCM levels were shown to increase in most cancer tissues, which were explained as a result of high membrane concentration during the proliferation of cancer cells. We found that Cho level was reduced in pancreatic cancer after radiotherapy, suggesting that proliferation of cancer cells was inhibited in response to radiotherapy. However, PC and GPC levels showed no significant change in tumor tissue after radiotherapy. This might be explained by a blockage of Cho-kinase and PC transferase, or by the consumption of PC through the CDP-Cho pathway[30,31]. Thus, we may deduce that increasing Cho and unchanged PC and GPC could be used as a unique profile of pancreatic cancer response to radiotherapy. Bet donates methyl groups for the remethylation of homocysteine to methionine and dimethylglycine, which supports proper liver and pancreatic function, cellular replication, and detoxification reactions. Because Cho is the precursor of Bet, the decrease of both Bet and Cho levels in pancreatic cancer after radiation treatment must be interrelated. Interestingly, the Ace level showed no significant difference between the normal pancreas and pancreatic cancer. However, Ace level dramatically increased with the radiation dose. The underlying significance of this needs to be further investigated.
In summary, although the number of samples in our study was limited, the potential of HRMAS NMR for the in vitro investigation of pancreatic disease response to radiotherapy should not be ignored. The above results clearly demonstrate that the metabolic profile changes of pancreatic cancer after radiotherapy were closely correlated with therapeutic effect through HRMAS 1H NMR and the PCA combined method. Because metabolite changes observed by HRMAS NMR always occur before morphological changes investigated by MRIS, HRMAS NMR will certainly be beneficial to pathological research, early diagnosis, and therapy evaluation of pancreatic diseases.
Therapeutic evaluations of radiotherapy are mainly: remission from the symptoms of pain and jaundice, solid tumor size and its survival time, and the lack of a specific targeted method. During the last three decades, there has been ongoing magnetic resonance spectroscopy research in malignant diseases. These studies provided valuable data on the biochemistry and metabolism of tumors, along with the effects on nutrients, hormones, and growth factors.
High-resolution magic angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (HRMAS 1H NMR) is a well-recognized technique in metabonomics studies in vitro, by which biopsy or postmortem samples of intact tissues are spun at the magic angle, resulting in a significant improvement in the resolution of the spectrum obtained for some of line-broadening factors such as dipole–dipole interactions and chemical shift anisotropy. Magnetic field inhomogeneities are also averaged out. This approach requires minimal sample preparation and, unlike convenient 1H NMR spectroscopy of tissue extracts, both aqueous and lipid-soluble metabolites can be observed simultaneously in situ.
Although HRMAS 1H NMR combined with principal components analysis (PCA) has demonstrated to be an efficient method for studying a wide variety of animal and human cancers, this combined method has not been reported to analyze the metabolic features of cancer response to therapy. Here, HRMAS 1H NMR and PCA were combined to highlight metabolite profiles of pancreatic cancer after radiotherapy, and by which the correlation between radiotherapy effect and metabolic change was analyzed, and the therapeutic scheme optimized.
The study has important implication for a reference guide on therapeutic evaluation by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy on pancreatic cancer in vivo.
The authors investigated whether metabolic profile changes of pancreatic cancer after radiotherapy were closely correlated with therapeutic effect through the HRMAS 1H NMR and PCA combined method. The outcome of the study is interesting and beneficial to pathological research, early diagnosis, and therapeutic evaluation of pancreatic diseases.
P- Reviewers Sun ZH, Supiot S S- Editor Zhai HH L- Editor Rutherford A E- Editor Zhang DN
| 1. | Greenlee RT, Murray T, Bolden S, Wingo PA. Cancer statistics, 2000. CA Cancer J Clin. 2000;50:7-33. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 2959] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 2746] [Article Influence: 114.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Wang L, Yang GH, Lu XH, Huang ZJ, Li H. Pancreatic cancer mortality in China (1991-2000). World J Gastroenterol. 2003;9:1819-1823. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 3. | Hirshberg B, Libutti SK, Alexander HR, Bartlett DL, Cochran C, Livi A, Chang R, Shawker T, Skarulis MC, Gorden P. Blind distal pancreatectomy for occult insulinoma, an inadvisable procedure. J Am Coll Surg. 2002;194:761-764. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 4. | Daly PF, Cohen JS. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy of tumors and potential in vivo clinical applications: a review. Cancer Res. 1989;49:770-779. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 5. | Kaplan O, Cohen JS. Metabolism of breast cancer cells as revealed by non-invasive magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1994;31:285-299. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 25] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Kaplan O, Navon G, Lyon RC, Faustino PJ, Straka EJ, Cohen JS. Effects of 2-deoxyglucose on drug-sensitive and drug-resistant human breast cancer cells: toxicity and magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies of metabolism. Cancer Res. 1990;50:544-551. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 7. | Ben-Horin H, Tassini M, Vivi A, Navon G, Kaplan O. Mechanism of action of the antineoplastic drug lonidamine: 31P and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance studies. Cancer Res. 1995;55:2814-2821. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 8. | Glaholm J, Leach MO, Collins DJ, Mansi J, Sharp JC, Madden A, Smith IE, McCready VR. In-vivo 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy for monitoring treatment response in breast cancer. Lancet. 1989;1:1326-1327. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 53] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 63] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Ng TC, Grundfest S, Vijayakumar S, Baldwin NJ, Majors AW, Karalis I, Meaney TF, Shin KH, Thomas FJ, Tubbs R. Therapeutic response of breast carcinoma monitored by 31P MRS in situ. Magn Reson Med. 1989;10:125-134. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 10. | Griffin JL, Mann CJ, Scott J, Shoulders CC, Nicholson JK. Choline containing metabolites during cell transfection: an insight into magnetic resonance spectroscopy detectable changes. FEBS Lett. 2001;509:263-266. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 81] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 82] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Waters NJ, Garrod S, Farrant RD, Haselden JN, Connor SC, Connelly J, Lindon JC, Holmes E, Nicholson JK. High-resolution magic angle spinning (1)H NMR spectroscopy of intact liver and kidney: optimization of sample preparation procedures and biochemical stability of tissue during spectral acquisition. Anal Biochem. 2000;282:16-23. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 106] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 108] [Article Influence: 4.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Cheng LL, Chang IW, Smith BL, Gonzalez RG. Evaluating human breast ductal carcinomas with high-resolution magic-angle spinning proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Magn Reson. 1998;135:194-202. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 137] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 103] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Sitter B, Bathen T, Hagen B, Arentz C, Skjeldestad FE, Gribbestad IS. Cervical cancer tissue characterized by high-resolution magic angle spinning MR spectroscopy. MAGMA. 2004;16:174-181. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 66] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 50] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Moka D, Vorreuther R, Schicha H, Spraul M, Humpfer E, Lipinski M, Foxall PJ, Nicholson JK, Lindon JC. Biochemical classification of kidney carcinoma biopsy samples using magic-angle-spinning 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 1998;17:125-132. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 111] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 112] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Tomlins AM, Foxall PJD, Lindon JC, Nicholson JK, Lynch MJ. High resolution magic angle spinning 1H nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of intact prostatic hyperplastic and cancer tissues. Anal Comm. 1998;35:113-115. [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 16. | Cheng LL, Lean CL, Bogdanova A, Wright SC, Ackerman JL, Brady TJ, Garrido L. Enhanced resolution of proton NMR spectra of malignant lymph nodes using magic-angle spinning. Magn Reson Med. 1996;36:653-658. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 163] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 167] [Article Influence: 6.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Chen JH, Enloe BM, Fletcher CD, Cory DG, Singer S. Biochemical analysis using high-resolution magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy distinguishes lipoma-like well-differentiated liposarcoma from normal fat. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:9200-9201. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 48] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 51] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Holmes E, Nicholls AW, Lindon JC, Ramos S, Spraul M, Neidig P, Connor SC, Connelly J, Damment SJ, Haselden J. Development of a model for classification of toxin-induced lesions using 1H NMR spectroscopy of urine combined with pattern recognition. NMR Biomed. 1998;11:235-244. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 19. | Holmes E, Nicholls AW, Lindon JC, Connor SC, Connelly JC, Haselden JN, Damment SJ, Spraul M, Neidig P, Nicholson JK. Chemometric models for toxicity classification based on NMR spectra of biofluids. Chem Res Toxicol. 2000;13:471-478. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 236] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 239] [Article Influence: 10.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Fang F, He X, Deng H, Chen Q, Lu J, Spraul M, Yu Y. Discrimination of metabolic profiles of pancreatic cancer from chronic pancreatitis by high-resolution magic angle spinning 1H nuclear magnetic resonance and principal components analysis. Cancer Sci. 2007;98:1678-1682. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 21. | Garrod S, Humpfer E, Spraul M, Connor SC, Polley S, Connelly J, Lindon JC, Nicholson JK, Holmes E. High-resolution magic angle spinning 1H NMR spectroscopic studies on intact rat renal cortex and medulla. Magn Reson Med. 1999;41:1108-1118. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 22. | Kaplan O, Kushnir T, Askenazy N, Knubovets T, Navon G. Role of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) in cancer diagnosis and treatment: 31P, 23Na, and 1H MRS studies of three models of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 1997;57:1452-1459. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 23. | Shinchi H, Takao S, Noma H, Matsuo Y, Mataki Y, Mori S, Aikou T. Length and quality of survival after external-beam radiotherapy with concurrent continuous 5-fluorouracil infusion for locally unresectable pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;53:146-150. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 115] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 121] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Ishikawa H, Suzuki Y, Nakayama Y, Nakamoto S, Kusaba T, Kakinuma S, Sakata Y, Mitsuhashi N, Niibe H. Intraoperative radiotherapy and bypass surgery for unresectable pancreatic cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2000;47:1151-1155. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 25. | Cienfuegos JA, Manuel FA. Analysis of intraoperative radiotherapy for pancreatic carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2000;26 Suppl A:S13-S15. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 26. | Ceha HM, van Tienhoven G, Gouma DJ, Veenhof CH, Schneider CJ, Rauws EA, Phoa SS, González González D. Feasibility and efficacy of high dose conformal radiotherapy for patients with locally advanced pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer. 2000;89:2222-2229. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 27. | Katz MH, Bouvet M. Novel gene therapy approaches to pancreatic cancer. Int J Gastrointest Cancer. 2003;33:89-97. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 28. | Loening NM, Chamberlin AM, Zepeda AG, Gonzalez RG, Cheng LL. Quantification of phosphocholine and glycerophosphocholine with 31P edited 1H NMR spectroscopy. NMR Biomed. 2005;18:413-420. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 29. | Cheng LL, Anthony DC, Comite AR, Black PM, Tzika AA, Gonzalez RG. Quantification of microheterogeneity in glioblastoma multiforme with ex vivo high-resolution magic-angle spinning (HRMAS) proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neuro Oncol. 2000;2:87-95. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 9] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Podo F. Tumour phospholipid metabolism. NMR Biomed. 1999;12:413-439. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 31. | Morvan D, Demidem A, Papon J, Madelmont JC. Quantitative HRMAS proton total correlation spectroscopy applied to cultured melanoma cells treated by chloroethyl nitrosourea: demonstration of phospholipid metabolism alterations. Magn Reson Med. 2003;49:241-248. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 47] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |