Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2013; 19(11): 1850-1854
Published online Mar 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1850
Published online Mar 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1850
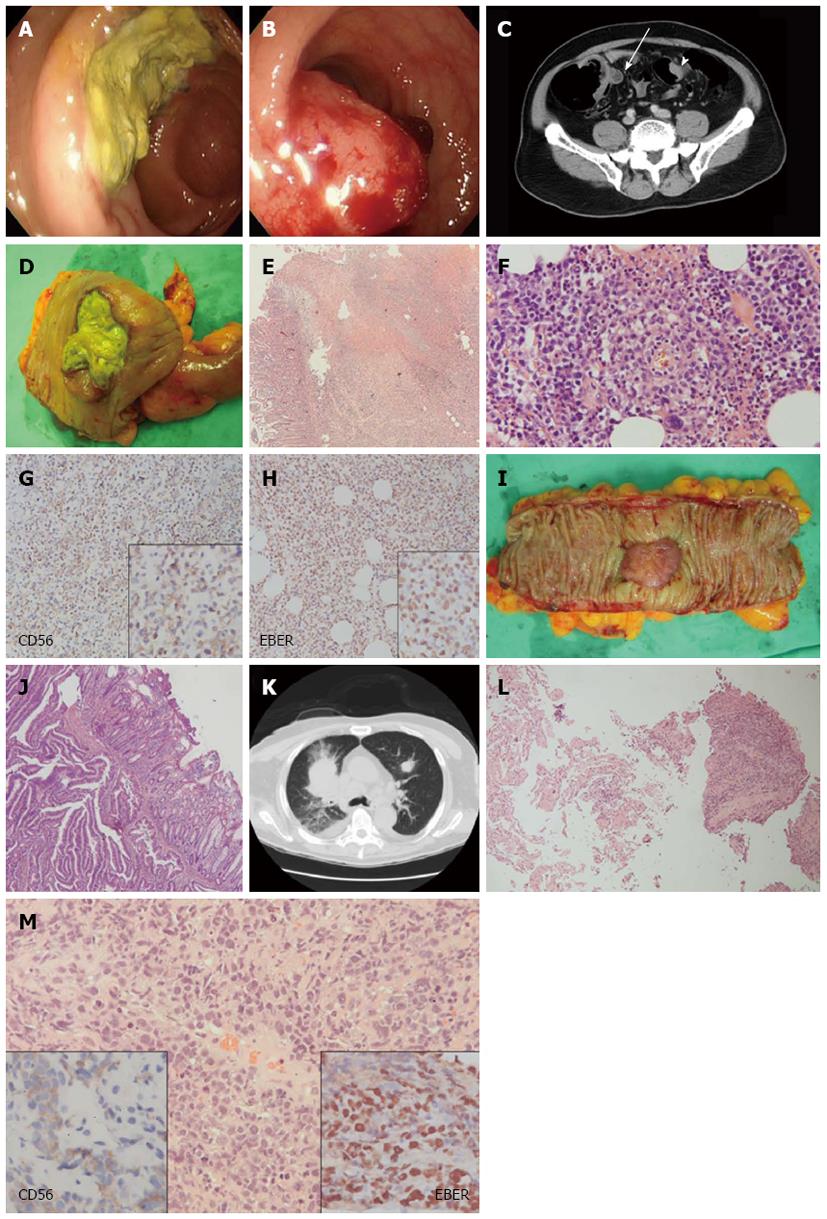
Figure 1 Clinical imaging studies and pathologic features of synchronous extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma and adenocarcinoma of the colon, as well as lung metastasis of the lymphoma.
A: Appearance of the proximal ascending colon on colonoscopy: A marked ulcerative mass coated with necrotic tissue; B: Appearance of the sigmoid colon on colonoscopy: A polypoid bleeding mass; C: Computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen revealing a mass in the proximal ascending colon (arrow on the left) and another mass in the sigmoid colon (arrowhead on the right); D: Surgical specimen of the proximal ascending colon showing an ulcerative mass; E: Histologically, a section of the tumor from the proximal ascending colon showing neoplastic lymphoid cells (right lower part) infiltrating the colonic mucosa (left part) accompanied by a necrotic ulcer (upper middle part), hematoxylin and eosin (HE) stain, × 40; F: Angioinvasion of the neoplastic lymphoid cells of the lymphoma, HE stain, ×400; G: CD56 reactivity of the lymphoma cells, × 200 (right lower inset, × 400); H: Epstein-Barr virus encoded RNA (EBER) reactivity of the lymphoma cells, × 200 (right lower inset, × 400); I: Surgical specimen from the sigmoid colon revealing a polypoid, hemorrhagic mass; J: Histology of the sigmoid colon tumor showing adenocarcinoma with infiltrative neoplastic glands, HE stain, × 40; K: Multiple lung metastases of the lymphoma on follow-up CT scan of the chest (the largest nodule on the right lung was biopsied); L: Histology of the lung biopsy showing lung parenchyma (on the left) and tumor cells (on the right), HE stain, × 100; M: Histologically, a section of the lung biopsy showing the ovoid nucleated neoplastic cells with high N/C ratio, HE stain, × 400, and reactivity of EBER (right lower inset, × 400) and CD56 (left lower inset, × 400).
- Citation: Tseng CE, Shu TW, Lin CW, Liao KS. Synchronous adenocarcinoma and extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma of the colon: A case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(11): 1850-1854
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i11/1850.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i11.1850