Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2012; 18(32): 4317-4322
Published online Aug 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i32.4317
Published online Aug 28, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i32.4317
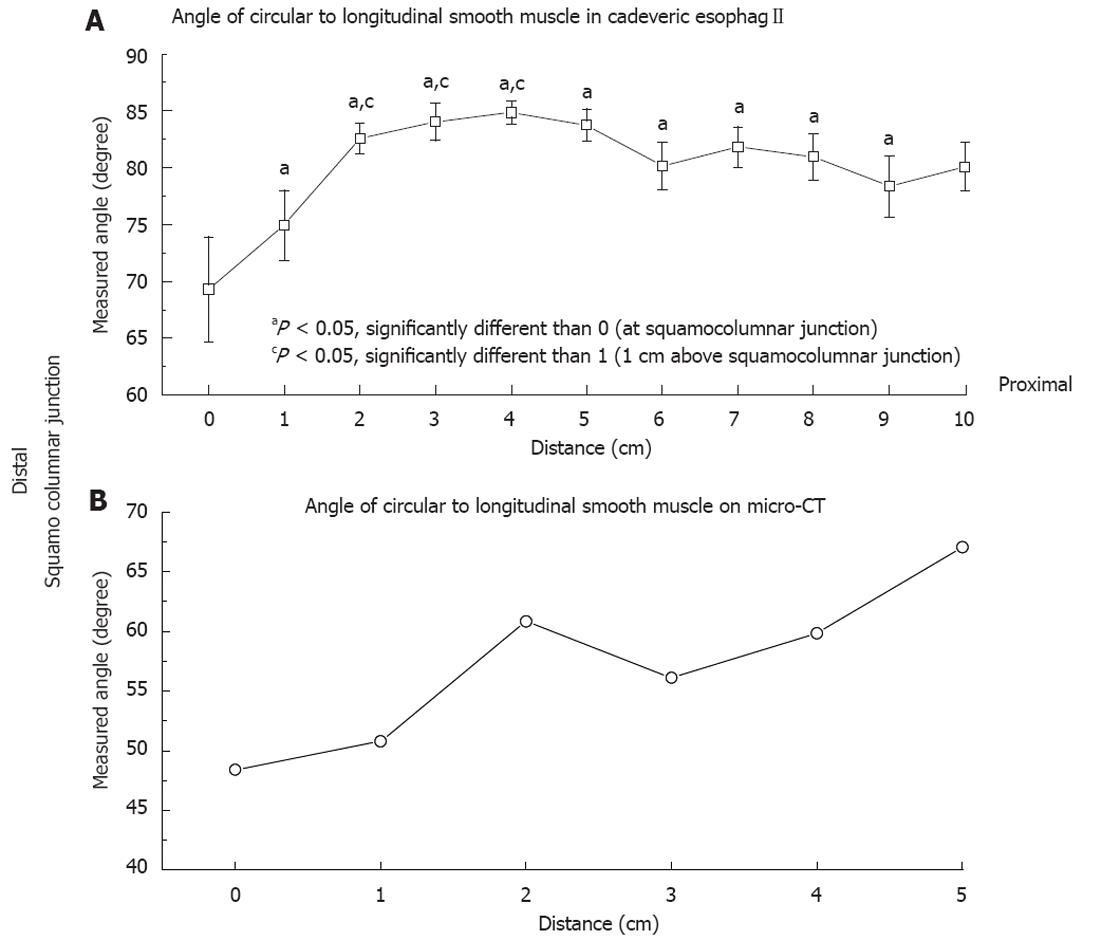
Figure 3 The average angle of the circular smooth muscle with respect to the longitudinal smooth muscle.
A: On cadaveric esophagi. The x-axis represents the distance from the squamocolumnar junction with 0 being the squamocolumnar junction. At 90 degrees the circular smooth muscle and longitudinal smooth muscle are perpendicular to each other. Therefore the smaller the angle the greater the deviation from the perpendicular and the greater the resulting shortening during peristaltic contraction; B: Measured using micro computed tomography. The x-axis represents the distance from the squamocolumnar junction with 0 being the squamocolumnar junction. CT: Computed tomography.
- Citation: Vegesna AK, Chuang KY, Besetty R, Phillips SJ, Braverman AS, Barbe MF, Ruggieri MR, Miller LS. Circular smooth muscle contributes to esophageal shortening during peristalsis. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(32): 4317-4322
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i32/4317.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i32.4317