Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2012; 18(30): 3977-3991
Published online Aug 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i30.3977
Published online Aug 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i30.3977
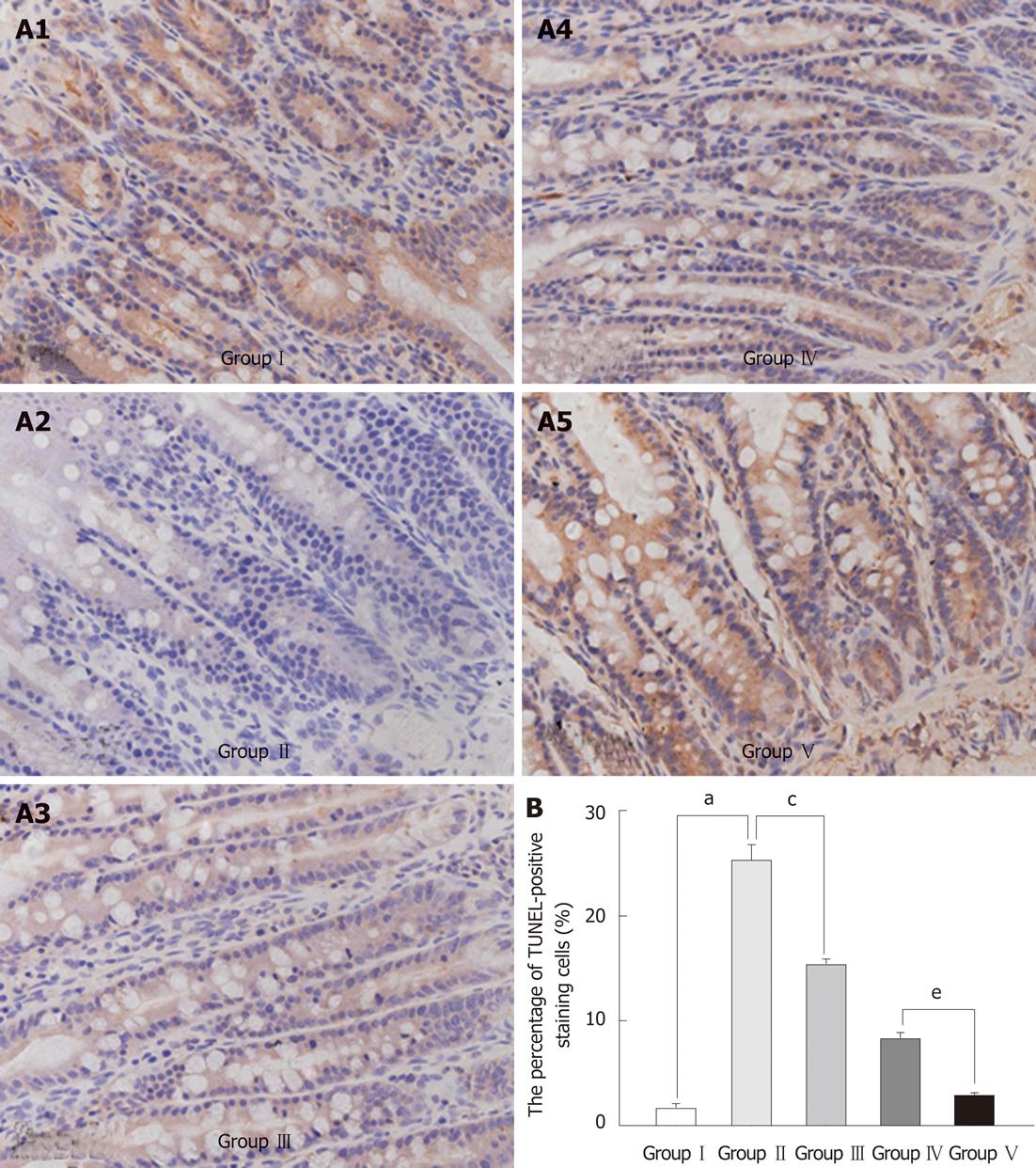
Figure 4 Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum on the apoptosis in the intestinal mucosal epithelium.
A: Ileum sections from each group stained using the terminal deoxyuridine nick-end labeling (TUNEL) method. TUNEL-positive cells were stained dark brown. A significantly higher number of TUNEL-positive cells was detected in tissues from group II animals compared with group III; and the number of TUNEL-positive cells in group IV was higher than in group V. Images shown represent at least three regions observed on the same slide; B: Statistical evaluation of effects of Lactobacillus plantarum (L. plantarum) on the apoptosis in the intestinal mucosal epithelium. Data in the bar graph represent mean ± SD of a minimum of three slides per group. aP < 0.05 Group I vs Group II; cP < 0.05 Group II vs Group III; eP < 0.05 Group IV vs Group V. Group I : Sham-operation; Group II: Bile duct ligation (BDL); Group III: BDL + L. plantarum; Group IV: BDL + internal biliary drainage (IBD); Group V: BDL + IBD + L. plantarum.
-
Citation: Zhou YK, Qin HL, Zhang M, Shen TY, Chen HQ, Ma YL, Chu ZX, Zhang P, Liu ZH. Effects of
Lactobacillus plantarum on gut barrier function in experimental obstructive jaundice. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(30): 3977-3991 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i30/3977.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i30.3977