Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2012; 18(27): 3527-3536
Published online Jul 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i27.3527
Published online Jul 21, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i27.3527
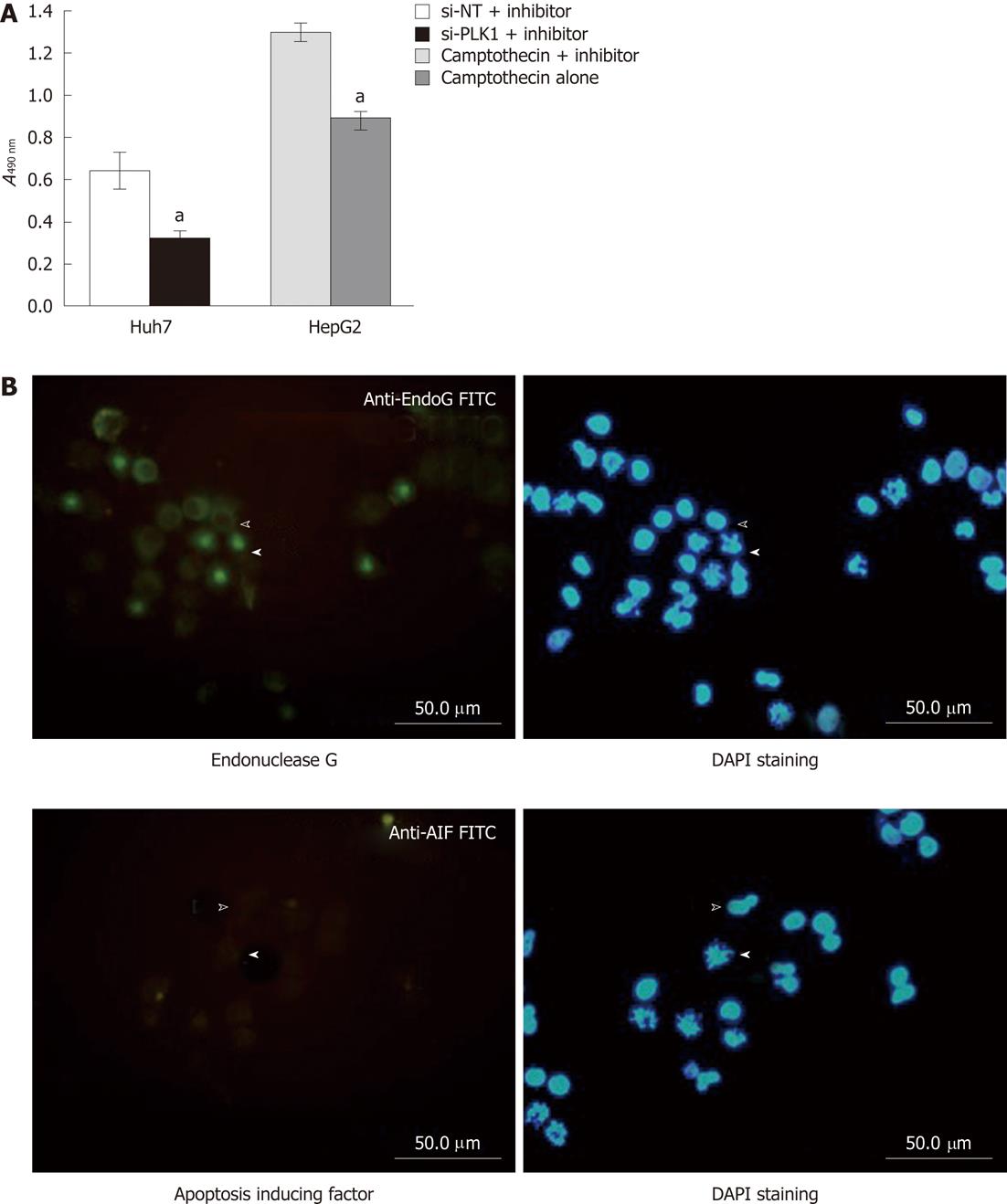
Figure 4 Lack of apoptosis protection and caspase-independent apoptosis.
A: Lack of apoptosis protection by pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FML after knockdown of polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1). The MTS cell proliferation assay in Huh-7 cells transfected with either short interfering non-targeting (si-NT) or short interfering-PLK1 (si-PLK1) in the presence of the pan caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK showed that the pan caspase inhibitor failed to protect si-PLK1 transfected Huh-7 cells from apoptosis. In contrast, HepG2 that were treated with camptothecin and Z-VAD-FMK were protected from apoptosis induced by camptothecin while those treated with camptothecin without Z-VAD-FMK were not protected from apoptosis. Data are shown as mean ± SE, using the Student t-test (aP < 0.05); B: Caspase-independent apoptosis likely due to endonuclease G. Huh-7 transfected with 50 nmol/L si-PLK1 for 24 h was probed with antibody against endonuclease G or apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) and subsequently visualized with fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated secondary antibody (left panels). The corresponding 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)-stained images are shown in the right panels. Block arrowheads and hollow arrowheads mark apoptotic and non-apoptotic Huh-7 cells respectively. Endonuclease G was positively stained in apoptotic cells and colocalized to the fragmented chromosomes (upper left panel), while AIF was found to be absent (lower left panel).
- Citation: Mok WC, Wasser S, Tan T, Lim SG. Polo-like kinase 1, a new therapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(27): 3527-3536
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i27/3527.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i27.3527