Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2012; 18(22): 2850-2858
Published online Jun 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i22.2850
Published online Jun 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i22.2850
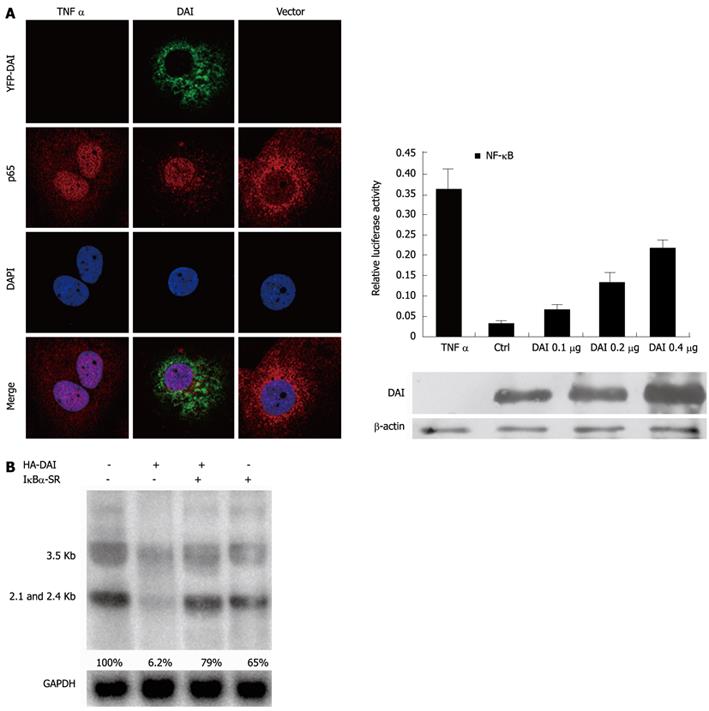
Figure 3 Inhibition of hepatitis B virus by DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors depends on activation of nuclear factor-κB.
A: NF-κB activity was induced by dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors (DAI). Forty-eight hours after transfection, NF-κB (p65) was stained as described. NF-κB dependent luciferase reporter plasmid pNF-κB-Luc was co-transfected with control DNA or different doses of hemagglutinin (HA)-DAI into 293T cells. Renilla luciferase-herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase promoter was transfected to monitor the transfection efficiency; B: Blockage of NF-κB activation abolished DAI-mediated suppression of hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication. Forty-eight hours after transfection, the levels of hepatitis B e antigen and hepatitis B surface antigen were examined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. HBV RNA was determined by Northern blotting hybridization. NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DAPI: 4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole; YFP: Yellow fluorescent protein.
- Citation: Chen QY, Liu YH, Li JH, Wang ZK, Liu JX, Yuan ZH. DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors inhibits hepatitis B virus replication. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(22): 2850-2858
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i22/2850.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i22.2850