Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2012; 18(22): 2850-2858
Published online Jun 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i22.2850
Published online Jun 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i22.2850
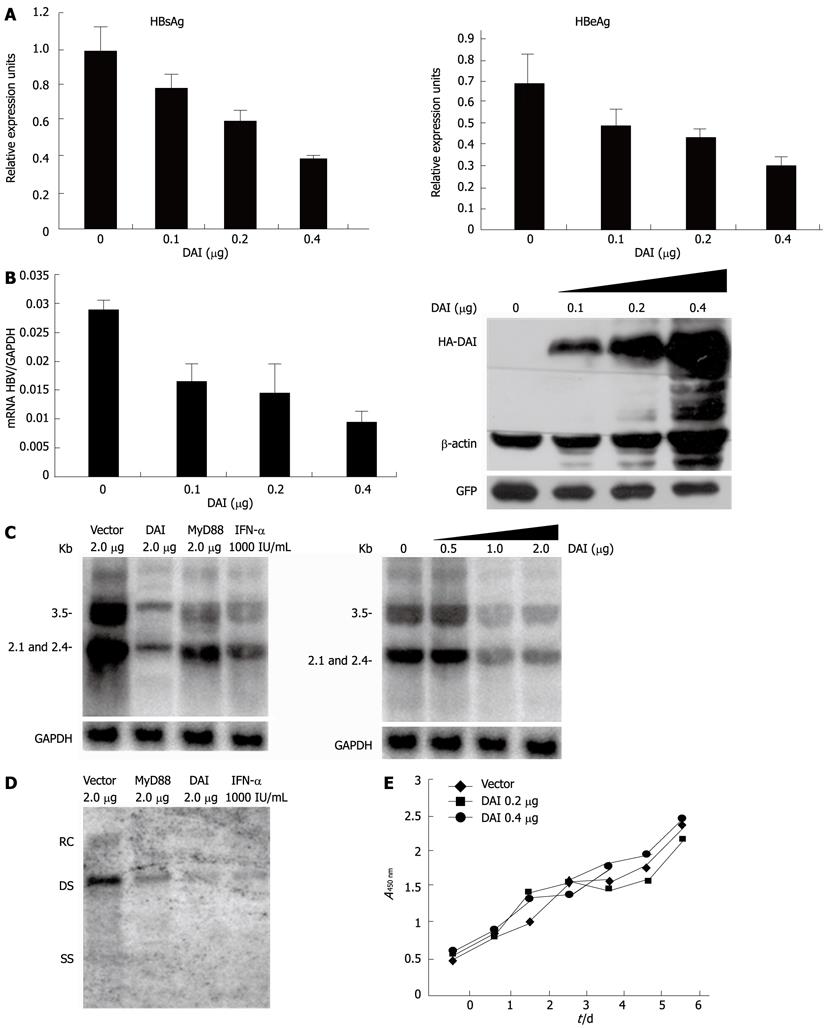
Figure 1 Expression of DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors in Huh7 cells can suppress hepatitis B virus replication.
A: ELISA analysis of HBV protein synthesis. GFP was transfected to monitor transfection efficiency; B: Real-time PCR analysis of HBV RNA. Huh7 cells were cotransfected with pHBV1.3 and different doses of hemagglutinin (HA)-DAI. Total RNA was extracted 48 h after transfection and HBV RNA was examined by real-time PCR; C: Northern blottings analysis of HBV RNA; Huh7 cells were cotransfected with pHBV1.3 and control DNA or MyD88 and HA-DAI. 1000 IU/mL IFN-α was added 12 h after transfection, and 48 h later, total RNA was extracted for Northern blotting hybridization. The positions of the HBV 3.5-, 2.4- and 2.1-kb RNA were indicated; D: Southern blotting analysis of HBV core particle associated DNA. Huh7 cells were treated as in C. HBV core particle associated DNA was analyzed 48 h later. Southern blotting was performed to detect HBV DNA as described. The positions of relaxed circular (RC), double stranded (DS) and single stranded (SS) DNAs were indicated; E: Effect of DAI on cell growth. Cell number was counted by adding cell counting kit-8 at 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 d after transfection. DAI: DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; ELISA: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; IFN: Interferon; GFP: Green fluorescent protein; HBsAg: Hepatitis B virus surface antigen; HBeAg: Hepatitis B virus e antigen; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; MyD88: Myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88.
- Citation: Chen QY, Liu YH, Li JH, Wang ZK, Liu JX, Yuan ZH. DNA-dependent activator of interferon-regulatory factors inhibits hepatitis B virus replication. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(22): 2850-2858
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i22/2850.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i22.2850