Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2011; 17(6): 681-690
Published online Feb 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i6.681
Published online Feb 14, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i6.681
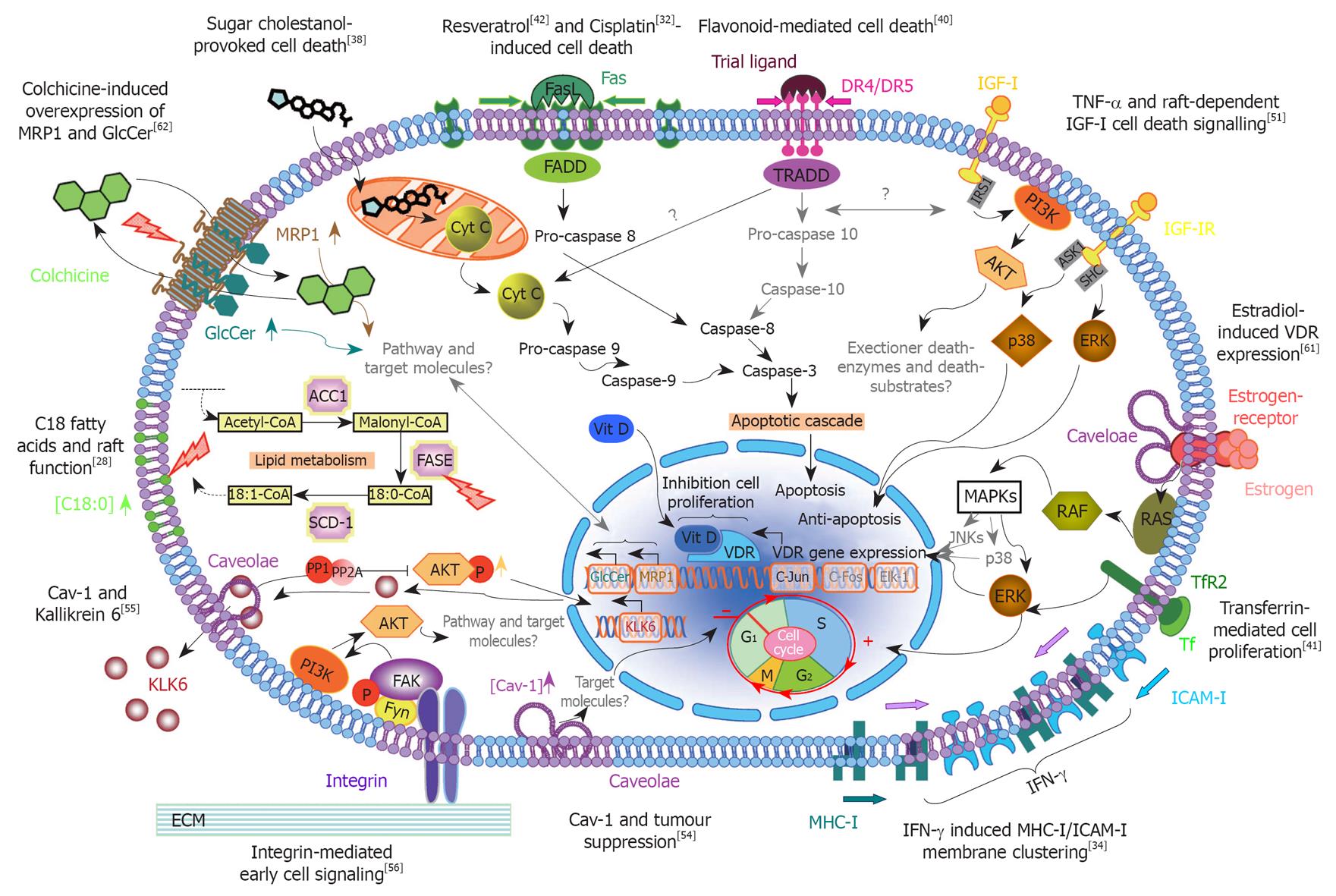
Figure 2 Scheme outlining the various membrane microdomain-mediated intracellular signaling pathways in colorectal cancer.
This diagram summarizes what has been reported to date in the literature about the different intracellular signaling pathways that are mediated by lipid rafts and the implications of these paths for the colon cancer cells’ state and fate. Briefly, the different observations of colorectal cancer (CRC) lipid rafts can be generally categorized under the following main topics of investigation: cell death-mediated mechanisms, caveolae in cancer cell growth and function, unique structure-function molecular associations, and intervention studies with bioactive compounds. Note that the text and connector arrows as shown in black are confirmed observations, whereas the gray denotes postulated signaling pathways and/or unknown molecular targets. The lipid bilayer of the cell membrane is depicted in light blue, membrane microdomains or lipid rafts in light purple, and the pear-shaped caveolae associated with these rafts in dark purple. For detailed descriptions of each of the individual cell signaling pathways, refer to the corresponding sections in this paper. The numbers in superscript refer directly to the original published papers. MRP: Multidrug-resistance protein; GlcCer: Glucosylceramide; FADD: Fas-associated protein with death domain; TRADD: Tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1-associated DEATH domain protein; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT: Serine/threonine protein kinase; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; IRS1: Insulin receptor substrate 1; ASK1: Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; SHC: Src homology 2 domain; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IGF-I: Insulin-like growth factor-I; VDR: Vitamin D receptor; Vit D: Vitamin D; RAF: Proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase; RAS: RAt sarcoma; TfR2: The second transferrin receptor; Tf: Transferrin; JNKs: c-Jun N-terminal kinases; ICAM-I: Intercellular adhesion molecule I; IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; MHC-I: Major histocompatibility complex I; FAK: Focal adhesion kinase; ECM: Extracellular matrix; FASE: Fatty acid synthase; SCD-1: Stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1; ACC1: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; Cav: Caveolin.
- Citation: Jahn KA, Su Y, Braet F. Multifaceted nature of membrane microdomains in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(6): 681-690
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i6/681.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i6.681