Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2011; 17(33): 3802-3809
Published online Sep 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3802
Published online Sep 7, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3802
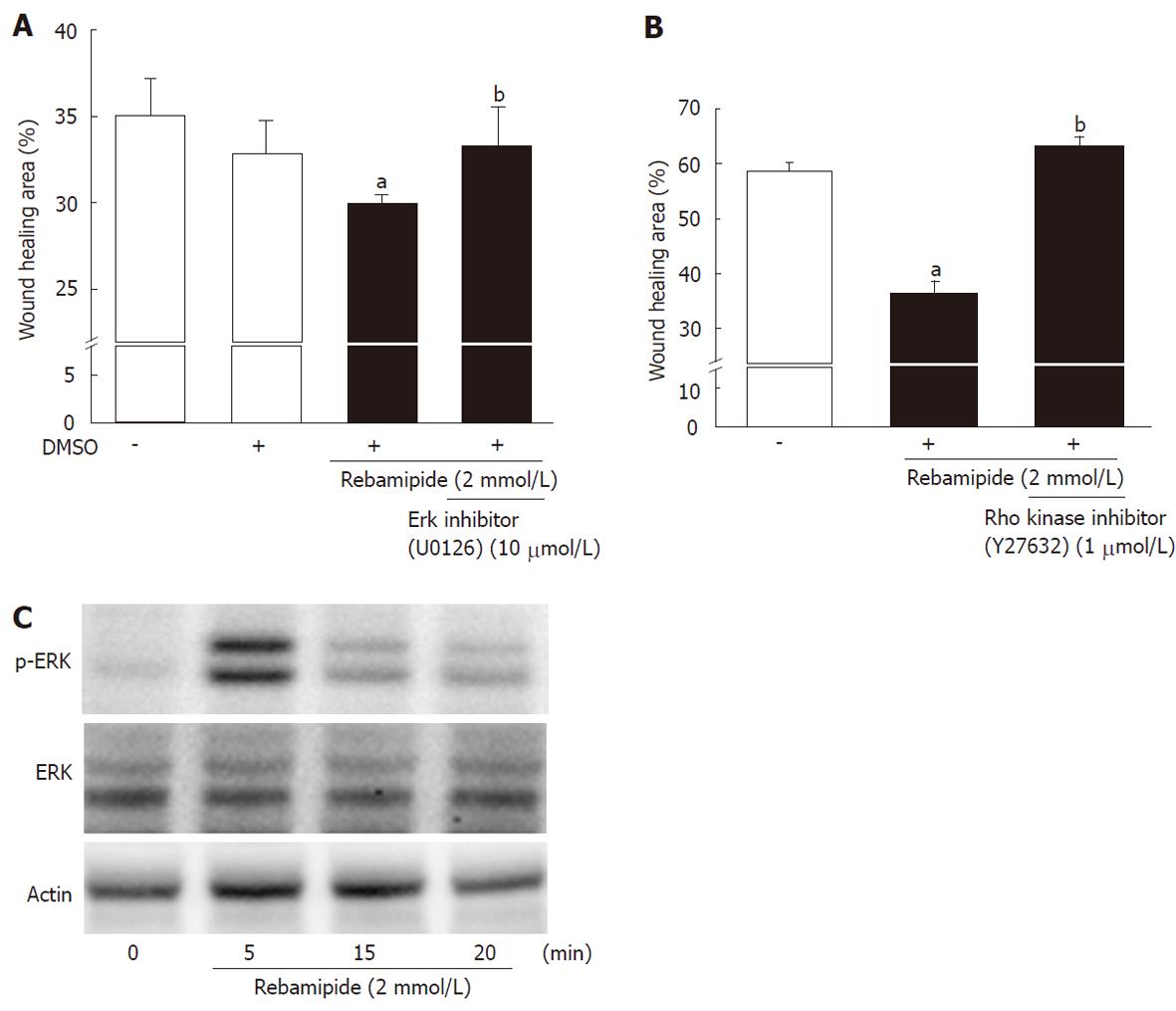
Figure 4 Involvement of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Rho in rebamipide-treated rat intestinal epithelial cells.
A: Rat intestinal epithelial (RIE) cells were treated with rebamipide (2 mmol/L) with or without an extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibitor (U01263, 10 μmol/L) after wound induction. The wound healing area (12 h later) was then monitored. Data represent the mean ± SE of four experiments. aP < 0.05 vs controls. bP < 0.05 vs the 2 mmol/Lrebamipide-treated group. B: Expression of p44/42 and phospho-p44/42 in RIE cells incubated with rebamipide (2 mmol/L) was measured using western blot analysis. Actin antibody was used as an internal control. Representative data from three observations is shown. C: RIE cells were treated with rebamipide (2 mmol/L) with or without Rho kinase inhibitor (Y27632, 1 μmol/L) after wound induction. The wound healing area (6 h later) was then monitored. Data represent the mean ± SE of four experiments. aP < 0.05 vs controls. bP < 0.05 vs the 2 mmol/L rebamipide-treated group. DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide.
- Citation: Takagi T, Naito Y, Uchiyama K, Okuda T, Mizushima K, Suzuki T, Handa O, Ishikawa T, Yagi N, Kokura S, Ichikawa H, Yoshikawa T. Rebamipide promotes healing of colonic ulceration through enhanced epithelial restitution. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(33): 3802-3809
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i33/3802.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3802