Copyright
©2011 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2011; 17(3): 300-312
Published online Jan 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i3.300
Published online Jan 21, 2011. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i3.300
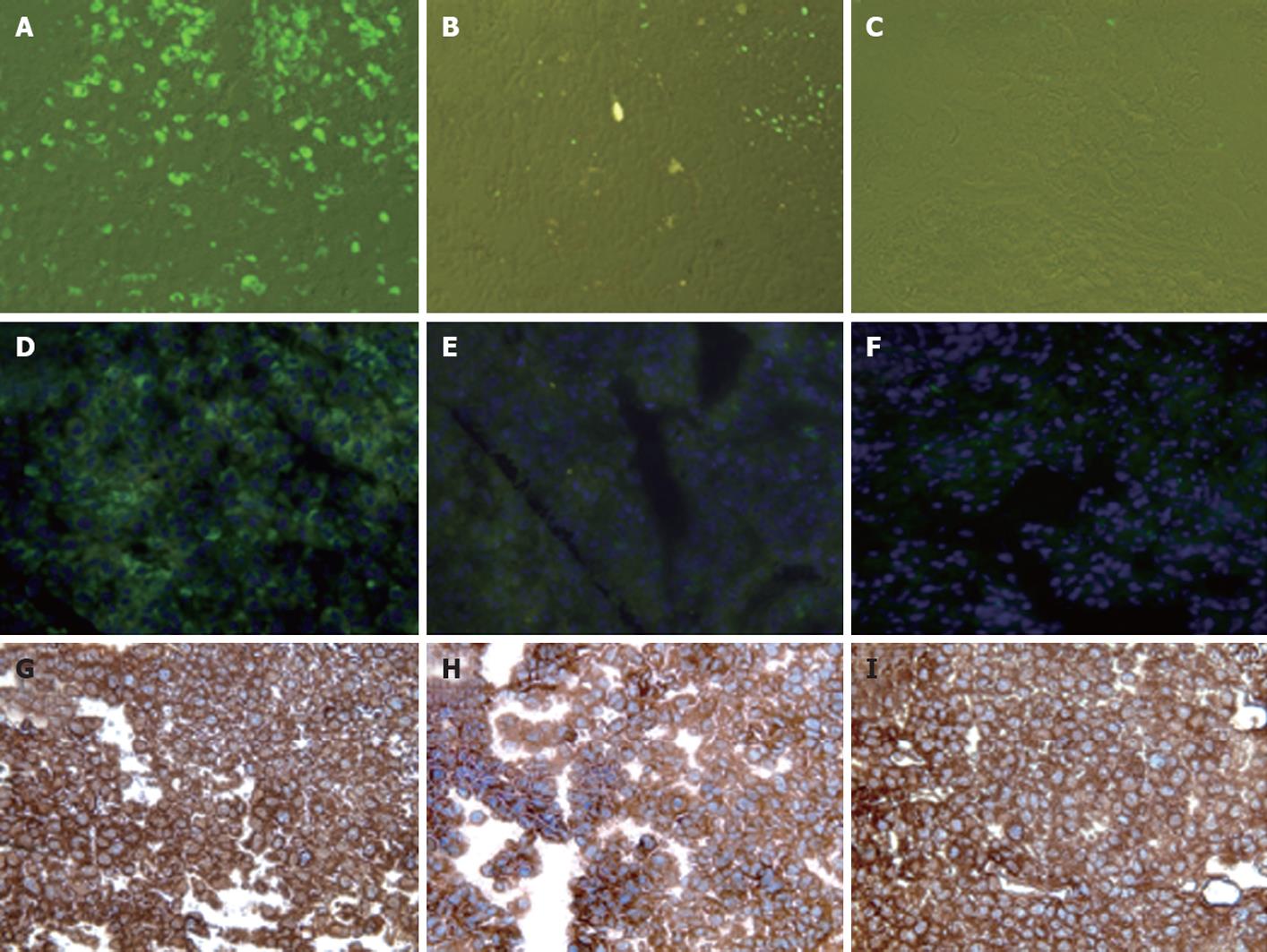
Figure 5 Interferon-α inhibits hepatitis C virus-green fluorescence protein expression in human hepatocellular xenografts formed subcutaneously in SCID mice.
Mouse-adapted replicon cells were injected subcutaneously into SCID mice, which then developed visible tumors after 2 wk. The mice were injected intraperitoneally with a total dose of 15 000 IU interferon-α (IFN-α) in 100-μL volumes, three times weekly. Tumors were harvested after 1 and 2 wk of IFN treatment and examined for green fluorescence protein (GFP) expression and viral RNA by RPA and real-time polymerase chain reaction. A, D: Expression of GFP in the frozen sections of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) xenografts before IFN-α treatment; B, E: Expression of GFP 1 wk after IFN-treatment; C, F: Expression of GFP after 2 wk IFN-treatment. The middle panel shows DAPI staining of the nucleus. IFN inhibited hepatitis C virus RNA replication and GFP expression in the liver tumors at 7 and 14 d; G-I: Intracytoplasmic expression of human albumin in the HCC xenografts formed by subcutaneous injection of in vivo adapted Huh-7 replicon cells.
- Citation: Hazari S, Hefler HJ, Chandra PK, Poat B, Gunduz F, Ooms T, Wu T, Balart LA, Dash S. Hepatocellular carcinoma xenograft supports HCV replication: A mouse model for evaluating antivirals. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17(3): 300-312
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v17/i3/300.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i3.300