Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2010; 16(28): 3553-3560
Published online Jul 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i28.3553
Published online Jul 28, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i28.3553
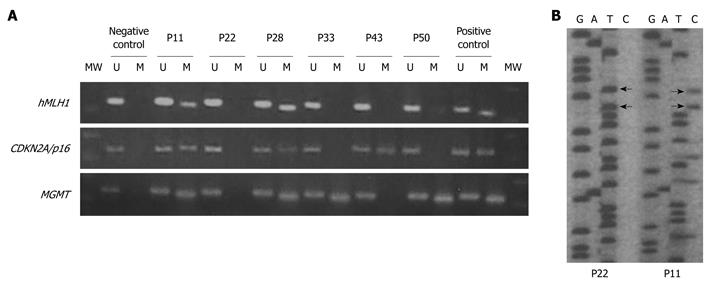
Figure 2 Methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction and sequence analysis.
A: Methylation specific polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for hMLH1, CDKN2A/p16 and MGMT promoter methylation. In this panel, the MSI-H patients P11 and P28 show promoter hypermethylation for hMLH1, CDKN2A/p16, and MGMT. The low-level MSI (MSI-L) patient P33 shows promoter hypermethylation for MGMT. The MSI stable (MSS) patient P22 does not show promoter hypermethylation for any gene, whereas the MSS patient P43 shows promoter hypermethylation only for CDKN2A/p16.The healthy MSS patient P50 shows promoter hypermethylation only for MGMT; B: Sequence analysis of methylation-specific PCR (MSP) PCR products of hMLH1 promoter. The sequence analysis of MSP products for patients P22 (unmethylated) and P11 (methylated) reveals the complete transition of non-methylated cytosines to thymine (indicated by arrows) after bisulfite treatment. There also cytosines that are partially methylated, as indicated from the co-existence of T and C. The sequence from the bottom to top: 5’-TGG tGT TTG AtG TtG TGT TtG tGG GTA GT-3’ P22 (unmethylated); 5’-TGG t(C)GT TTG At(C)G Tt(C)G TGT TCG CGG GTA GT-3’ P11 (methylated); 5’-TGG CGT TTG ACG TCG TGT TCG CGG GTA GT-3’ (wild type). Lower case letters represent thymines derived from unmethylated cytosines, the letters in parenthesis represent partially methylated cytosines and the bolds the CpG islands. MW: Molecular weight; M: Methylated promoter; U: Unmethylated promoter.
-
Citation: Psofaki V, Kalogera C, Tzambouras N, Stephanou D, Tsianos E, Seferiadis K, Kolios G. Promoter methylation status of
hMLH1 ,MGMT , andCDKN2A /p16 in colorectal adenomas. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(28): 3553-3560 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i28/3553.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i28.3553