Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2010; 16(15): 1845-1853
Published online Apr 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i15.1845
Published online Apr 21, 2010. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i15.1845
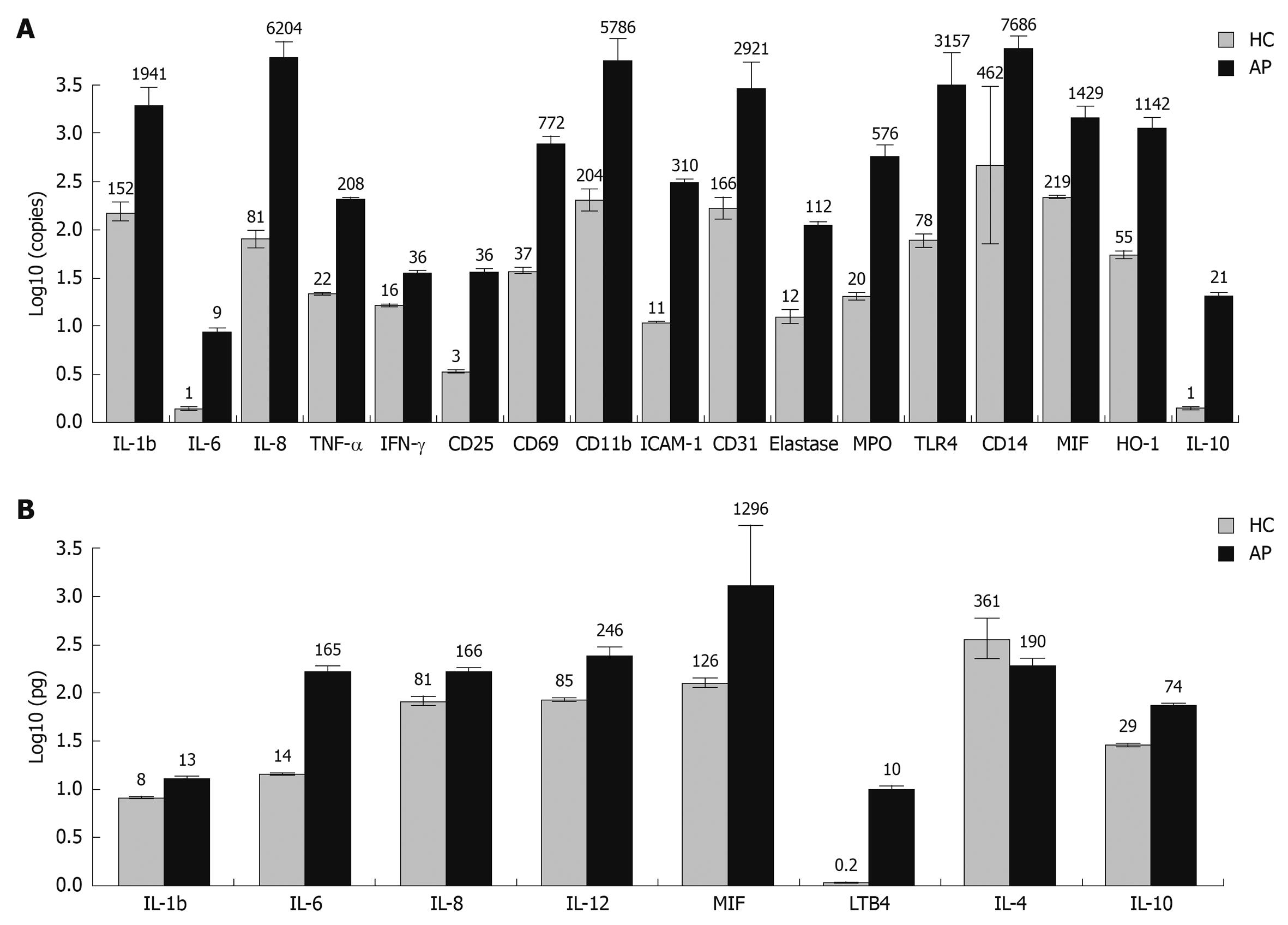
Figure 1 Cytokine expression at mRNA and protein level in peripheral blood of healthy subjects and acute pancreatitis (AP) patients.
A: Gene expression in peripheral blood leukocytes of healthy subjects and AP patients. Gene expression at mRNA level of 25 different cytokines, adhesion molecules, lymphocyte activation markers, and other biologically active substances known to be linked to the inflammatory response were assessed by quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (QRT-PCR) in peripheral blood leukocytes of AP patients and healthy controls. A median 18-fold (range: 2-77) increase in mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory molecules was observed in the AP group in comparison to healthy control subjects (HC). Activation of the anti-inflammatory system and some cytoprotective molecules was also notable in the AP patient group. Cytokine mRNA expression levels with statistically significant differences between AP and healthy control groups are shown; B: Cytokine concentration in blood serum of healthy controls and AP patients. Expression of eight different soluble molecules at protein level was assessed in serum of AP patients and healthy subjects using the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method. A median 3-fold (range: 2-59) increase in protein expression of pro-inflammatory molecules was observed in the AP group when compared to HC. Cytokine expression levels with statistically significant differences between AP and healthy control groups are shown. IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; IFN-γ: Interferon-γ; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; MIF: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor.
- Citation: Dambrauskas Z, Giese N, Gulbinas A, Giese T, Berberat PO, Pundzius J, Barauskas G, Friess H. Different profiles of cytokine expression during mild and severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16(15): 1845-1853
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v16/i15/1845.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i15.1845