Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2008; 14(44): 6786-6801
Published online Nov 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6786
Published online Nov 28, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6786
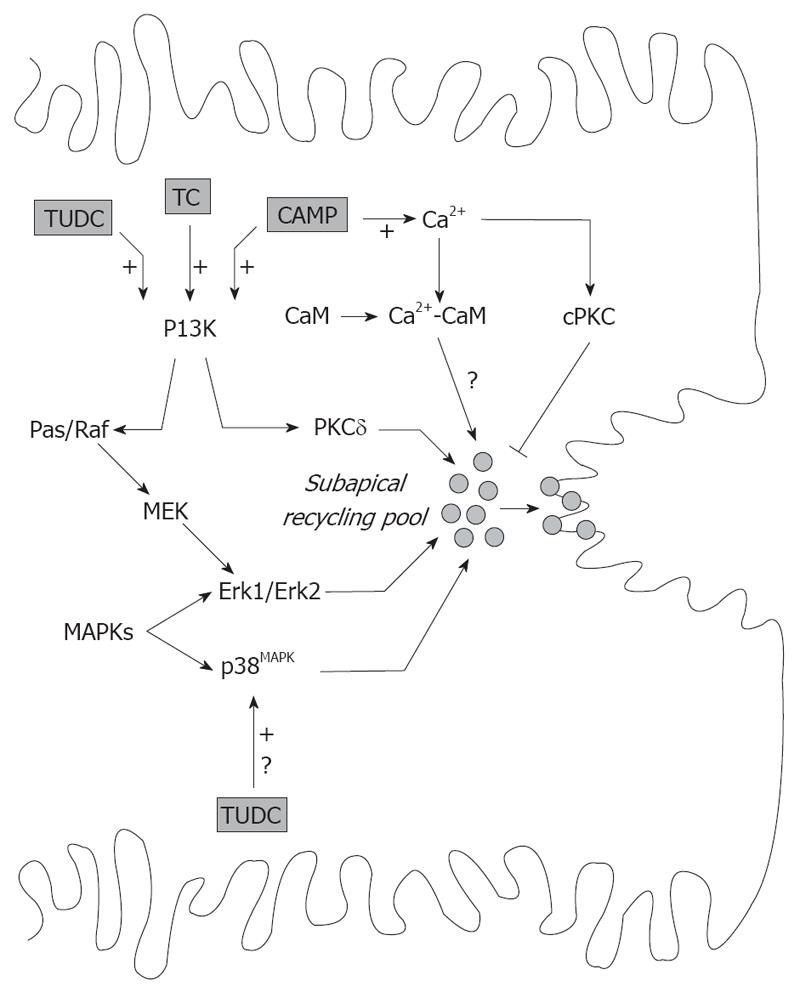
Figure 4 Signaling pathways involved in the exocytic insertion of canalicular transporters promoted by cAMP and by TC and TUDC.
cAMP effect involves elevation in cytosolic Ca2+ and activation of the PI3K-dependent pathway. Formation of the CaM complex promotes apical insertion of transporters via unidentified mediators, and is counter-regulated by activation of cPKC. PI3K promotes exocytic insertion of canalicular transporters by activation of PKCδ and Erk-1 and Erk-2 of MAPK, via the Ras/Raf- MAPK kinase (MEK)-Erk-1/2 pathway. TC and TUDC also evoke the PI3K-dependent signaling pathway and promote insertion of canalicular transporters via the Ras/Raf-MEK-Erk-1/2 pathway. TUDC also stimulates canalicular carrier insertion by activation of MAPKs of the p38MAPK type, by an unknown mechanism.
- Citation: Roma MG, Crocenzi FA, Mottino AD. Dynamic localization of hepatocellular transporters in health and disease. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(44): 6786-6801
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i44/6786.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.6786