Copyright
©2008 The WJG Press and Baishideng.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2008; 14(3): 390-400
Published online Jan 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.390
Published online Jan 21, 2008. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.390
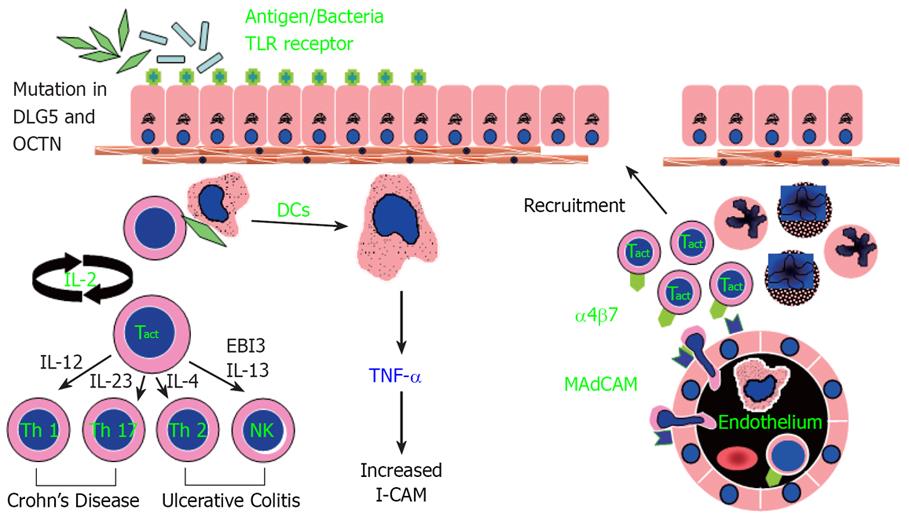
Figure 1 Working hypothesis of inflammatory bowel disease.
A defect occurs in sampling of gut luminal antigen, possibly mediated by enhanced Toll-like receptor activity and controlled by other genetic factors (mutations in DLG5 and OCTN). Over-response to antigens results in stimulated dendritic cells (DC) that recruits and generates various T-cell subtypes, which then initiate a cascade of immunologic events leading to mucosal inflammation. Adhesion molecules such as intercellular cell adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM1) are important for circulating mononuclear and polymorphonuclear cells to adhere and migrate to the inflamed gut mucosa. Crohn’s disease (CD) is a predominately Th1 and Th17 mediated process, while ulcerative colitis (UC) appears to be predominately mediated through Th2 and NK T-cells.
- Citation: Shih DQ, Targan SR. Immunopathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14(3): 390-400
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v14/i3/390.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.14.390