Copyright
©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2007; 13(39): 5196-5207
Published online Oct 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i39.5196
Published online Oct 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i39.5196
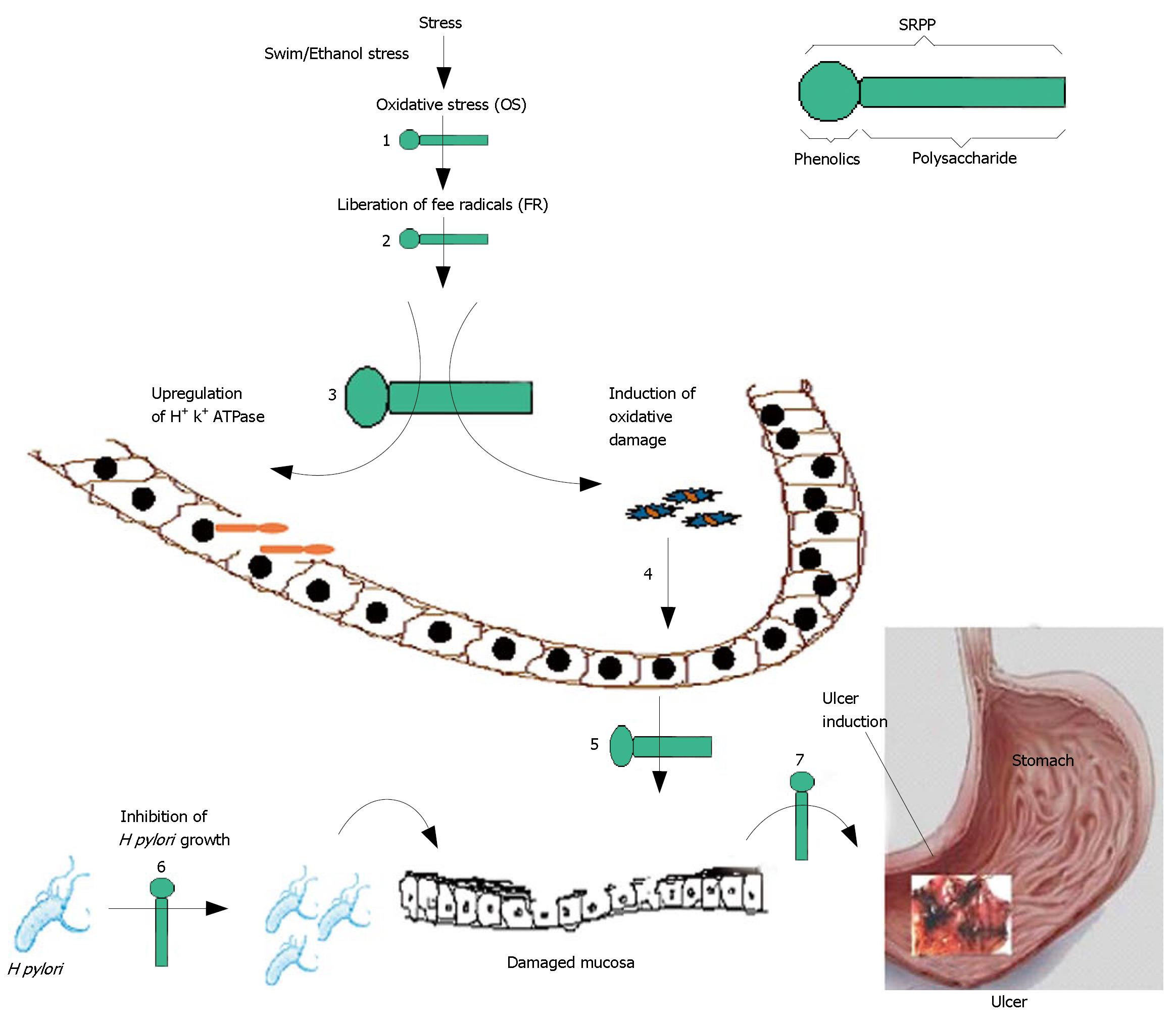
Figure 1 Scheme representing various steps of ulcer pathogenicity and multi-step anti-ulcer action by SRPP (•-); (•) and (-) represents phenolic and polysaccharide portions of SRPP respectively.
Swim/Ethanol stress leading to OS (1) and liberation of FR (2). FR upregulated H+, K+-ATPase (3) and induced oxidative damage to mucosa (4) leading to mucosal damage (5). H pylori may invade on to damaged mucosa and together may cause ulcers (7). SRPP has ability to inhibit steps 1-7 including the growth of H pylori in vitro (6).
-
Citation: Srikanta B, Siddaraju M, Dharmesh S. A novel phenol-bound pectic polysaccharide from
Decalepis hamiltonii with multi-step ulcer preventive activity. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(39): 5196-5207 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i39/5196.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i39.5196